Key Highlights:
- Florida Governor Ron DeSantis and Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick declare H-1B visa program a “scam” that undermines American workers
- New wage-based selection system proposed to replace random lottery, potentially affecting millions of Indian professionals
- Indians represent over 70% of H-1B visa approvals, making them primary targets of proposed immigration reforms
H-1B System Under Unprecedented Attack From Republican Leadership
The H-1B visa program faces its most significant challenge yet as top Republican officials launch coordinated attacks against the system, specifically targeting Indian workers who dominate the program. Florida Governor Ron DeSantis and Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick have publicly condemned the H-1B visa program as a “total scam,” marking a dramatic escalation in the Trump administration’s immigration crackdown.
Speaking to Fox News, DeSantis explicitly criticized companies for gaming the H-1B visa system while laying off American workers. “These companies game the system. Some of these companies are laying off large numbers of Americans while also hiring new H-1B workers and renewing existing H-1B visas,” DeSantis declared, adding that “most of them are from one country, India”. This direct targeting of Indian professionals represents a significant shift in how H-1B visa criticism is being framed by Republican leadership.
Commerce Secretary Lutnick reinforced these attacks, stating that “the current H-1B visa system is a scam that lets foreign workers fill American job opportunities” and emphasizing that “hiring American workers should be the priority of all great American businesses”. These statements signal a comprehensive effort to reshape America’s high-skilled immigration system, with Indian professionals bearing the brunt of proposed reforms.
The timing of these attacks coincides with growing political pressure to prioritize American workers, as the H-1B visa program has become a lightning rod for broader immigration debates in the United States.
Proposed Wage-Based Reform System Threatens Indian Professionals
- Elimination of lottery system: Random selection process replaced with wage-tier prioritization
- Salary-based allocation: Higher-paying positions receive priority in visa distribution
The Trump administration is advancing a comprehensive overhaul of the H-1B visa selection process, moving from the current random lottery system to a wage-based allocation model that could fundamentally alter who receives these coveted work permits. Under the proposed system, visa allocation would prioritize applicants based on salary levels, starting with Level 4 (highest wage offers) and working down through Level 3, Level 2, and Level 1 positions.
This wage-based H-1B visa system aims to ensure that visas are granted primarily to the most skilled and highest-paid professionals, potentially raising the average starting salary for those granted visas from around $106,000 to roughly $172,000. The Department of Homeland Security has already received approval from federal reviewers for this proposal, which mirrors similar efforts attempted during Trump’s first presidency.
The proposed H-1B visa program reforms would particularly impact recent graduates and entry-level professionals, who typically command lower starting salaries. This change could effectively shut out thousands of young Indian engineers, tech consultants, and researchers who have traditionally used the H-1B visa program as their primary pathway to American employment. Critics warn that this wage-based selection process would disadvantage recent international college graduates and could violate existing legal statutes.
Implementation of this H-1B visa system would require publication in the Federal Register followed by a 30-60 day public comment period before any final regulation could take effect. The proposed changes represent the most significant modification to the H-1B visa program in decades, with implications extending far beyond individual applicants to affect entire industries dependent on skilled foreign workers.
Statistical Evidence Reveals Scale of Indian Dependency on H-1B Program
- Demographic dominance: Indians account for over 70% of all H-1B visa approvals since 2015
- Registration trends: Significant fluctuations in H-1B visa applications reflect changing immigration policies
Official government data reveals the extraordinary extent to which Indian professionals dominate the H-1B visa program, making them particularly vulnerable to proposed reforms. Indians have consistently accounted for over 70% of all H-1B visa program approvals since 2015, with this percentage reaching 72.3% of the 386,000 H-1B visas granted in 2023. In fiscal year 2023, Indians comprised 68,825 (58%) of initial employment visas and 210,000 (79%) of extensions.
The scale of H-1B visa demand has fluctuated dramatically in recent years, reflecting changing immigration policies and economic conditions. USCIS data shows total registrations peaked at 780,884 in fiscal year 2024 before dropping to 479,953 in fiscal year 2025. Despite this decrease, eligible registrations remained substantial at 470,342, demonstrating continued strong demand for the H-1B visa program among foreign workers.
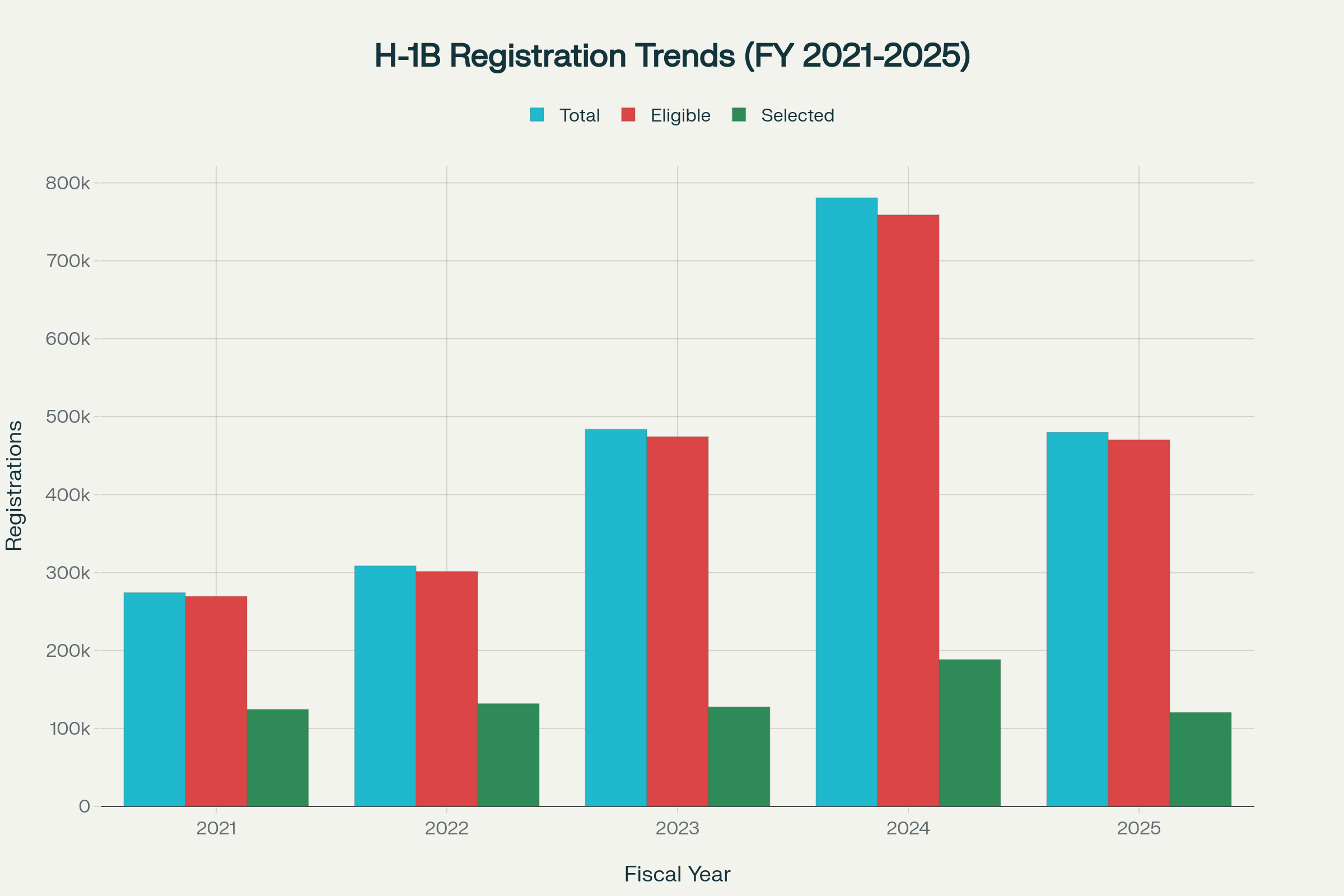
H-1B Visa Registrations and Selection Trends (2021-2025)
The selection process has become increasingly competitive, with nearly 400,000 H-1B applications approved in fiscal year 2024, most representing renewal applications for existing workers. This data underscores the program’s critical role in maintaining America’s skilled workforce, particularly in technology sectors where Indian professionals have established dominant positions.
The H-1B visa system’s annual cap of 85,000 new visas (65,000 regular cap plus 20,000 for advanced degree holders) creates intense competition, with USCIS rejecting almost two-thirds of applications in recent years due to overwhelming demand. This scarcity has intensified political debates about the program’s fairness and effectiveness.
Economic and Industry Impact of Proposed H-1B Reforms
- Technology sector disruption: Major IT companies face operational challenges and increased costs
- Wage inflation concerns: Prioritizing higher-paid workers could drive up compensation requirements
The proposed H-1B visa program reforms threaten to disrupt entire industries that have built business models around skilled foreign workers, with Indian IT companies bearing the greatest impact. Major firms like TCS, Infosys, and Wipro, which regularly send employees to the United States on H-1B visas for client projects, could face significantly increased operational costs and reduced flexibility in project staffing.
Commerce Secretary Lutnick’s criticism extends beyond the H-1B visa program to include the broader green card system, claiming that average American workers earn $75,000 annually while average green card recipients earn $66,000. This wage comparison forms part of a broader argument for implementing a new “gold card” system designed to attract higher-earning immigrants while potentially excluding lower-wage workers.
The H-1B visa system changes could force companies to hire more expensive local talent in the United States, potentially slowing project execution and service delivery across multiple industries. Smaller enterprises and sectors traditionally offering lower compensation, such as education and non-profit organizations, may find it increasingly difficult to access skilled foreign workers under a wage-based allocation system.
These H-1B visa reforms also threaten the pathway many Indian students use to transition from academic study to professional employment in America. Many rely on Optional Practical Training followed by H-1B visa program sponsorship to establish long-term careers in the United States. Stricter rules could push these graduates to return to India or migrate to other countries like Canada or the UK, potentially depriving American employers of skilled talent while strengthening competitor nations.
Final Perspective on America’s Immigration Crossroads
The coordinated attack on the H-1B visa system by Republican officials represents more than immigration policy adjustment—it signals a fundamental reassessment of America’s relationship with global talent. The proposed wage-based reforms, while aimed at protecting American workers, risk creating unintended consequences that could undermine the nation’s competitive advantage in attracting skilled professionals. As Indian workers face unprecedented scrutiny and potential exclusion from the H-1B visa program, the broader question emerges: will America’s pursuit of immigration restriction ultimately strengthen or weaken its position in the global economy? The answer may determine not only the fate of hundreds of thousands of foreign professionals but also the future trajectory of American innovation and economic growth in an increasingly competitive international landscape.


