Key Highlights:
- China’s Cyberspace Administration orders ByteDance, Alibaba and major tech firms to halt all Nvidia AI chip purchases immediately
- The ban eliminates Nvidia’s $5-10 billion annual Chinese revenue stream, representing 15% of global chip sales
- Chinese domestic AI chip companies surge with $240 billion stock market rally following showcase of indigenous alternatives
Regulatory Framework Behind China Bans Nvidia AI Chips
- China’s internet regulator issued mandatory compliance orders targeting all Nvidia artificial intelligence processors
- The restriction extends beyond previous guidance, encompassing RTX Pro 6000D and all future Nvidia AI chip variants
China bans Nvidia AI chips through comprehensive regulatory action by the Cyberspace Administration, delivering direct orders to technology giants including ByteDance, Alibaba, Baidu, and Tencent. The regulatory framework requires immediate cessation of all testing procedures, procurement activities, and deployment plans involving Nvidia’s artificial intelligence processors. This represents Beijing’s most decisive move in forcing technological independence from American semiconductor suppliers.
The scope of restrictions demonstrates how China bans Nvidia AI chips across multiple product categories, not limiting enforcement to specific models. Chinese authorities targeted Nvidia’s RTX Pro 6000D, the company’s specially modified chip designed to comply with US export restrictions, effectively closing the last significant sales channel for Nvidia in China. The Cyberspace Administration’s enforcement extends to cloud service providers, data center operators, and artificial intelligence research institutions throughout China.
Beijing’s regulatory strategy reveals coordinated policy implementation where China bans Nvidia AI chips while simultaneously promoting domestic alternatives through state-directed procurement. State-owned enterprises received instructions to prioritize Chinese semiconductors, with China Unicom announcing a $390 million data center project utilizing 23,000 domestically manufactured AI processors. This coordination ensures that when China bans Nvidia AI chips, domestic companies immediately benefit from redirected demand and government-backed contracts.finance.
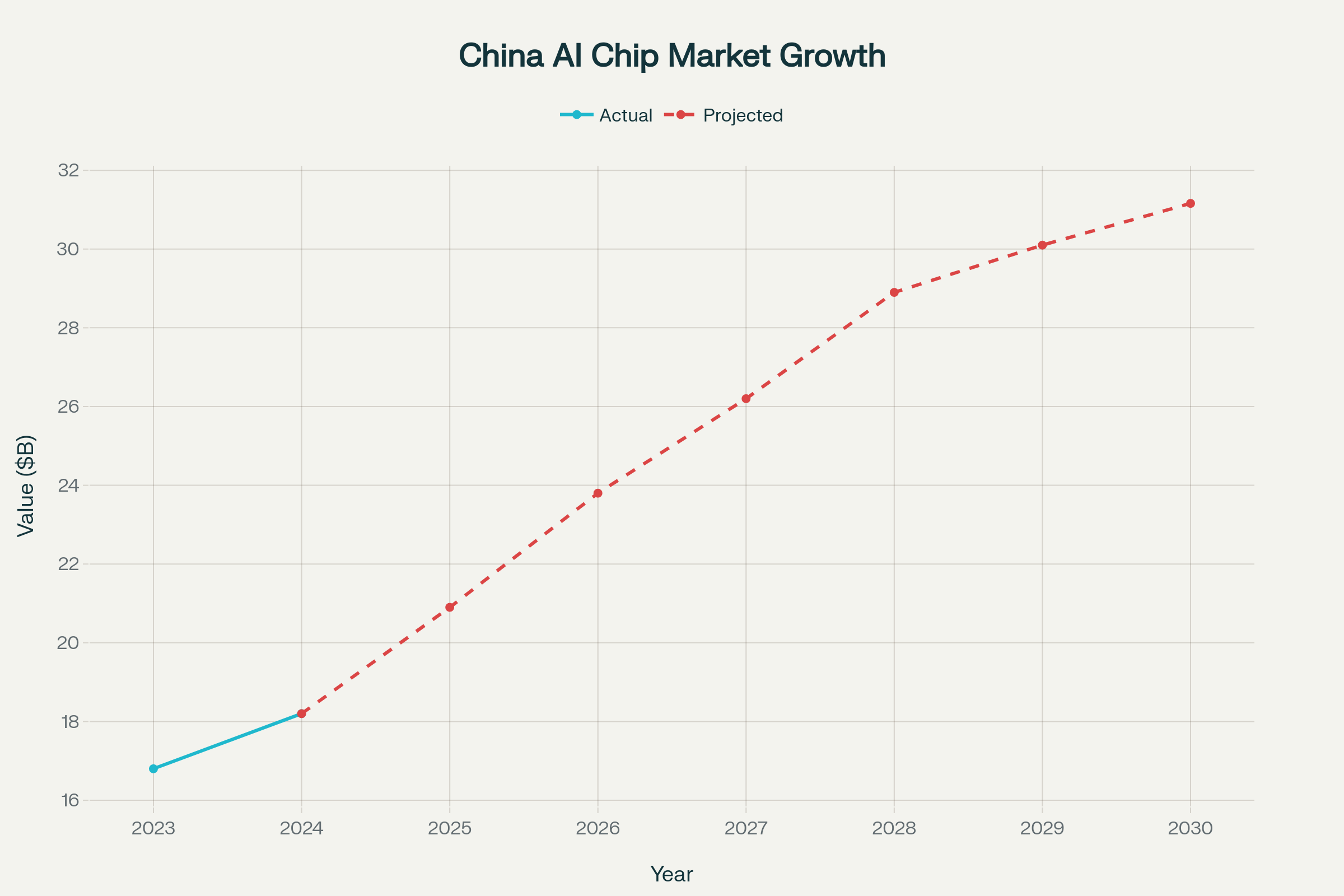
China AI Chip Market Growth Trajectory Despite Nvidia Restrictions
Economic Devastation as China Bans Nvidia AI Chips
- Nvidia faces $5-10 billion annual revenue loss from Chinese market elimination
- Company stock declined 3% immediately following ban announcement, erasing $75 billion market capitalization
The financial implications intensify dramatically as China bans Nvidia AI chips, eliminating the company’s access to the world’s second-largest AI market. Nvidia generated approximately $8.5 billion in Chinese revenue during 2024, representing 15% of global sales, making the loss of this market segment a structural threat to future growth projections. The company previously sold over 1 million H20 chips in China during 2024, maintaining 66% market share despite facing export restrictions.
Market analysts project severe long-term consequences as China bans Nvidia AI chips, forcing the company to write down $4.5 billion in unsold inventory specifically manufactured for Chinese compliance requirements. Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang acknowledged the company has instructed analysts to exclude Chinese revenue from financial forecasts, describing the situation as “a bit of a roller coaster” during a London press conference. The elimination occurs precisely when global AI chip demand reaches $150 billion in 2025, representing missed growth opportunities valued at tens of billions annually.
The ripple effects extend beyond immediate revenue loss as China bans Nvidia AI chips, forcing fundamental business model restructuring. Nvidia must accelerate development of less powerful Blackwell variants designed for export compliance, while shifting strategic focus toward Middle Eastern and Indian markets where AI infrastructure demand remains robust. However, these alternative markets cannot compensate for China’s scale, where the AI chip market reaches $18.2 billion in 2024 with projected growth to $31.16 billion by 2030.
Domestic Renaissance Accelerates as China Bans Nvidia AI Chips
- Chinese AI chip companies experience record growth with Cambricon achieving 4,400% revenue increase
- Huawei unveils three-year development roadmap targeting direct competition with banned Nvidia processors
The strategic consequences multiply as China bans Nvidia AI chips, catalyzing unprecedented growth in domestic semiconductor capabilities. Chinese companies collectively generated over $240 billion in stock market gains following public demonstrations of advanced AI chip technologies, with Huawei revealing comprehensive three-year development roadmaps featuring “super clusters” and high-performance AI accelerators. This surge reflects investor confidence that domestic alternatives possess sufficient capabilities to replace restricted American technology.finance.
Manufacturing capacity expansion accelerates dramatically as China bans Nvidia AI chips, with domestic producers scaling production to meet government-directed demand. Cambricon Technologies reported record profits of 1.03 billion yuan in the first half of 2025, representing a dramatic turnaround from previous losses driven by 4,400% revenue growth. The company’s Siyuan 690 processor targets direct competition with Nvidia’s H100 series, while achieving validation from China’s telecommunications authority as compatible with DeepSeek AI frameworks.
State coordination ensures systematic market transition as China bans Nvidia AI chips, channeling procurement toward indigenous suppliers through strategic partnerships. Alibaba’s T-Head division secured contracts to supply 72% of processors for China Unicom’s massive Xining data center project, demonstrating how government policy creates guaranteed customer bases for domestic chip manufacturers. Huawei sold 200,000 AI chips in 2024 despite offering lower performance per dollar compared to restricted Nvidia products, indicating price sensitivity drives adoption alongside regulatory compliance.
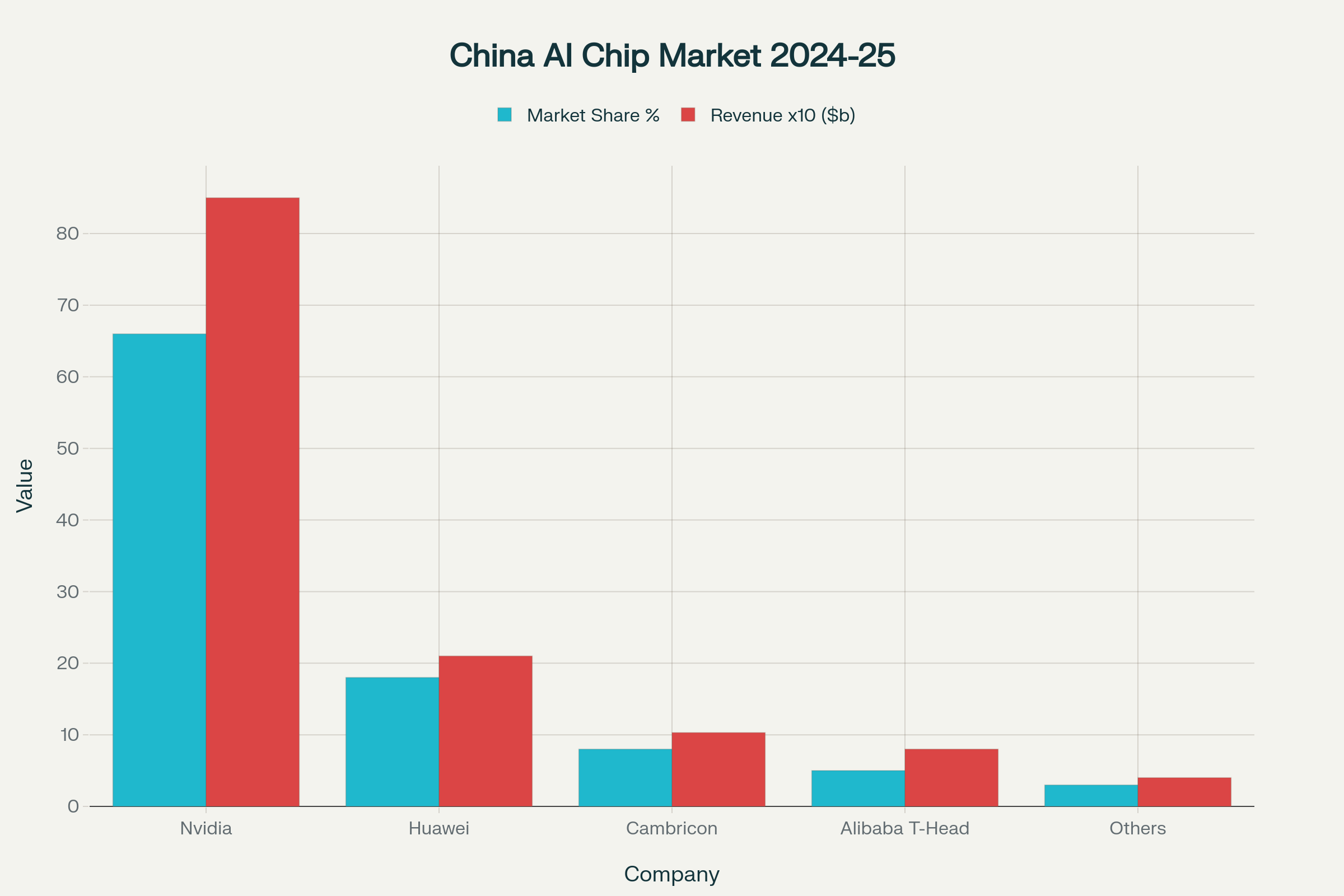
China AI Chip Market Share Competition Between Nvidia and Domestic Players
Geopolitical Implications as China Bans Nvidia AI Chips
- US-China technological decoupling accelerates with reciprocal semiconductor export restrictions
- Both nations prioritize technological sovereignty over economic efficiency in critical AI infrastructure
The geopolitical ramifications intensify as China bans Nvidia AI chips, representing escalatory response to American export controls implemented since October 2022. The United States restricted Chinese access to advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment and high-performance computing systems, targeting China’s artificial intelligence and military modernization capabilities. China’s retaliatory action demonstrates Beijing’s willingness to sacrifice short-term economic efficiency for long-term technological independence.
Strategic competition deepens as China bans Nvidia AI chips, forcing both nations toward parallel technological ecosystems with limited interoperability. American export controls specifically target China’s ability to acquire advanced lithography equipment from companies like ASML, while restricting access to cutting-edge graphics processing units essential for AI development. Chinese authorities responded with export controls on critical semiconductor materials including gallium and germanium, emphasizing national security justifications similar to American restrictions.
The decision reflects broader transformation as China bans Nvidia AI chips, signaling confidence that domestic alternatives have achieved sufficient performance thresholds to support national AI ambitions. Chinese researchers published 23,695 AI-related academic papers in 2024, exceeding combined output from the United States, United Kingdom, and European Union, demonstrating sustained innovation capacity despite technological restrictions. This research productivity suggests China’s artificial intelligence ecosystem continues advancing through indigenous development rather than dependence on foreign technology.
Republican leadership characterizes the situation as China positioning itself as a “peer-to-peer adversary” of the United States, emphasizing Chinese disregard for intellectual property protections and trade agreements. House Speaker Mike Johnson asserted China bears responsibility for deteriorating bilateral relations, reflecting bipartisan American consensus on confronting Chinese technological advancement through export controls and alliance coordination.
Final Assessment
China bans Nvidia AI chips represents a definitive moment in global technological competition, demonstrating Beijing’s commitment to semiconductor independence despite short-term performance compromises. The regulatory action eliminates Nvidia’s access to China’s $18.2 billion AI chip market while forcing acceleration of domestic alternatives that achieved remarkable financial performance in 2025. Chinese companies like Cambricon and Huawei demonstrated capability to scale production and achieve technological breakthroughs when supported by coordinated government policy and guaranteed procurement contracts.
The ban’s economic implications extend beyond immediate revenue losses, fundamentally reshaping global semiconductor supply chains and innovation ecosystems. Nvidia must restructure its business model while Chinese companies benefit from protected domestic markets and state-directed investment, creating parallel technological development paths with limited convergence. The decision reflects broader geopolitical priorities where both nations prioritize technological sovereignty over economic efficiency, accelerating bifurcation in critical artificial intelligence infrastructure.
Long-term consequences suggest China bans Nvidia AI chips will strengthen rather than weaken Chinese technological capabilities through forced innovation and domestic market protection. The $240 billion stock market rally following demonstrations of Chinese AI chip capabilities indicates investor confidence in indigenous alternatives, while government coordination ensures sustainable revenue streams for domestic manufacturers. This technological decoupling creates new competitive dynamics that will reshape global artificial intelligence development for decades to come.

