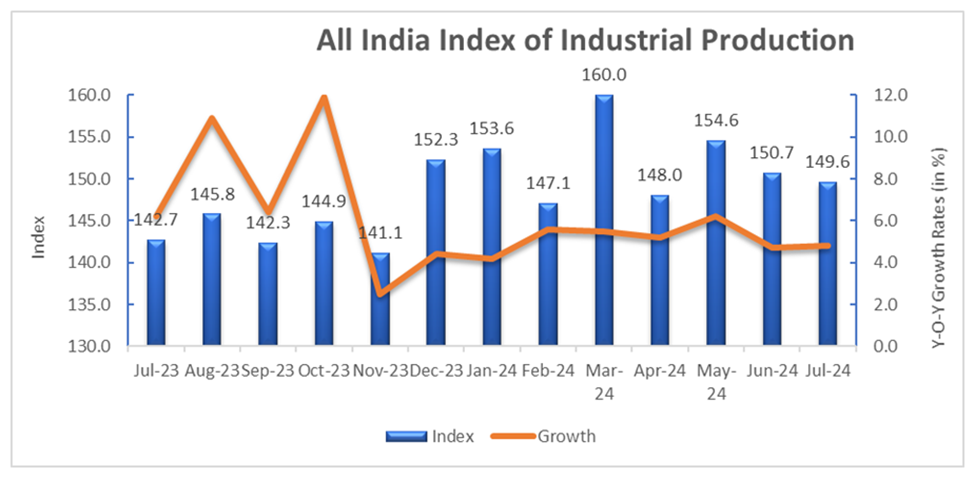
India’s industrial production showed steady growth in July 2024, with the Index of Industrial Production (IIP) recording a rise of 4.8 per cent. The IIP is a statistical analysis that tracks and shows changes in industrial sector production. A growing IIP indicates increased industrial production, economic growth, and improved productivity.
Sector analysis
Manufacturing sector
The manufacturing sector contributed the largest share of the IIP, crucial to its growth in July 2024. The automotive, textile, electronics, and pharmaceutical industries are the manufacturing sector’s industries that show rapid production activity. India’s middle class is rapidly increasing its demand for consumer goods like electronics, automobiles, and clothing. This demographic shift boosts manufacturers to expand their production and innovate with affordable and new products. Rapid urbanization requires construction materials and home-furnishing goods, which foster the manufacturing sector.
However, India’s manufacturing sector faces several challenges. Inadequate infrastructure, poor road conditions, and insufficient port facilities cause costs and delays. Everyone knows the central government launched the semi-high speed train Vande Bharat, which is pretty good. However, train delays and accidents have increased previously. The government invests a massive budget on railways and infrastructure but never matches the demand. Frequent power cuts hamper the manufacturing sector’s production. India’s regulatory framework is very complex. Taxation, labour laws, and environmental clearances make it difficult for manufacturers. India’s manufacturing sector never adapts to new advanced technology like AI and IoT.
Indian manufacturers invested very little in research and development, so making new innovative products aligned with global markets is challenging. India imports raw materials and high-tech components. It is not a robust supply chain, so sometimes delays and disruptions happen due to geopolitical issues or climate changes. Small and medium enterprises acquire a large part of the manufacturing sector but don’t have skilled labor and massive capital to invest and meet customer demand.
The government should take the necessary steps to reduce these issues. The government should renovate the railway infrastructure, improve punctuality, increase the container capacity of existing ports, and develop new ports. The concerned authority must mitigate inconsistent power supply. The government should relax rules and regulations for manufacturers to invest in India.
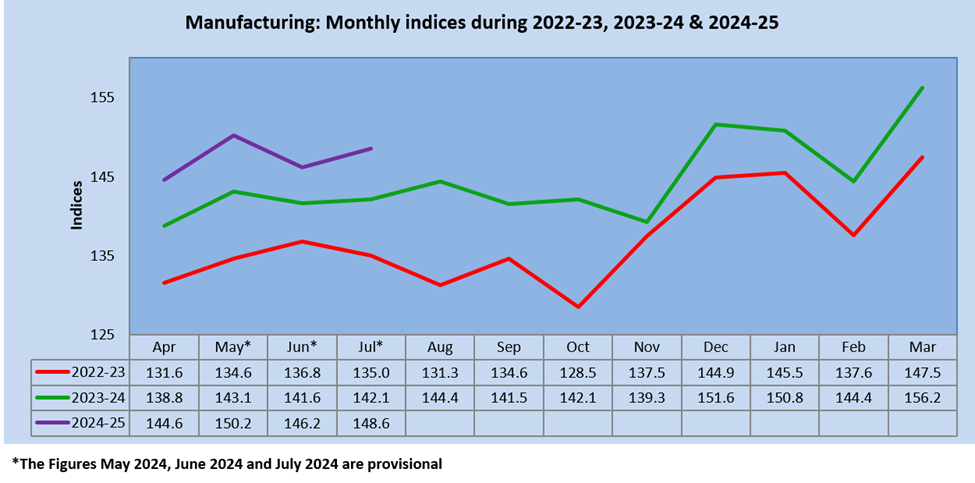
The manufacturing sector’s IIP growth rate for July 2024 is 4.6%. The top three positive contributors for July 2021 are “Manufacture of basic metal” (6.4%), “Manufacture of coke and refined petroleum products” (6.9%), and “Manufacture of electrical equipment” (28.3%).
Mining sector
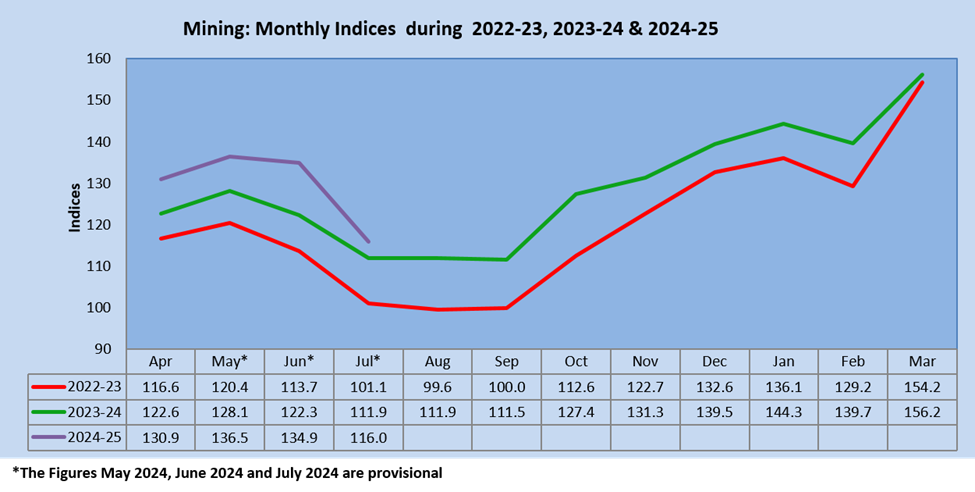
India’s mining industry, which encompasses coal, crude oil, and other minerals, has seen a surge in production due to favorable government policies and customers’ increased demand. It holds a significant percentage in the IIP calculation, around 14.37%. The other two, manufacturing and electricity, make up the rest per cent. The growth rate of the mining sector for the month of July 2024 is 3.7%. The mining sector includes extracting minerals, coals, ores and other natural resources.
The overall production performance depends upon key minerals like coal, natural gas and petroleum. The mining sector provides raw materials, essential or primary components for various industries, including energy, construction and steel. If India’s mining sector performs well, then India’s import cost will be reduced, and export income will increase. It has a significant contribution to the national GDP.
However, due to increasing mining projects and activity, environmental degradation and health and safety issues have increased. The government approves any mining extraction projects. They only focus on maximizing extraction and never consider future side effects. This leads to overexploiting India’s mineral wealth and concerns long-term sustainability. The concerned authorities use the “growth-at-all-cost” approach, which is dangerous in the long run. The authorities only focus on growth and market share at the expense of portability.
This causes unsustainable business models that jeopardize long-term success. Due to mining projects rapidly increasing, forests are destroyed, water is contaminated, the ecosystem is damaged, and soils are barren. The expansion of the mining sector hampers India’s environmental health, climate and local biodiversity. The mining projects need massive land areas, meaning many rural communities lose their homeland. It creates conflicts over land rights.
It shows a glaring failure in governance and social responsibilities. Mismanagement, bureaucratic delays, corruption and lack of clear policies harm mining industries and the economy. In 2012, the Supreme Court of India banned Goa Iron Ore Mining. The mining companies in Goa exceeded their production limit and exploited resources without their licensed areas. The concerned authorities and regulators failed to balance production and the environment. This ban left thousands of workers unemployed. It created uncertainty and instability in the mining sector.
Growth in Index of Industrial Production is good for the mining sector, but the rapid growth without rule regulations on illegal mining expansion is dangerous for India’s mining health. Getting licenses and environmental clearances without a bribe becomes complicated and lengthy. Many conflicts exist between state and government policies regarding the environment, taxation, etc.
Fatal accidents and professional diseases are increasing daily, which shows the government’s inability or unwillingness to enforce safety standards in the workplace. Safety is mandatory in rules and regulations, but no safe and secure workplace exists in real mining places. The authorities never physically visit the mining area or know about these illegal practices.
Sometimes, the contractors exploit the workers and give them lower wages than minimum wages. Growth means overall growth, not only in a nation’s GDP but also in the condition of workers. Of course, we appreciate the government and workers and employees related to the mining sector, but they also invest in improving workers’ lives. The other countries have shifted to sustainable and greener practices, but India’s mining sector is stuck in an outdated energy-intensive model, increasing the carbon footprint.
The government implements more environmentally friendly technologies, such as renewable energy, water recycling, etc., which reduces water pollution and the overexploitation of petroleum and coal. They must enforce new strict environmental rules and regulations for mining projects. Now, days after mining, the companies leave the mining areas in unstable conditions. The government ensures that the mining companies restore the area by reforestation, habitats, and stabilization. The government must look into community displacement and Indigenous rights matters. The mining companies must obtain the consent of local communities before mining activities begin. The mining companies must provide fair compensation for the land. The Indian government must enforce stringent safety rules like protective equipment and emergency training.
Electricity sector
The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) for the electricity sector in India is a primary element of the sector’s performance. Growth in electricity generation and distribution activities emphasizes the economy of India. The industry sector needs more power for expansion. That means more industrial and commercial projects require more electricity consumption. Higher electricity consumption requires more resources like coal, petroleum, and natural gas. It increases job opportunities and boosts a robust economy. During extreme weather, customers’ demands change.
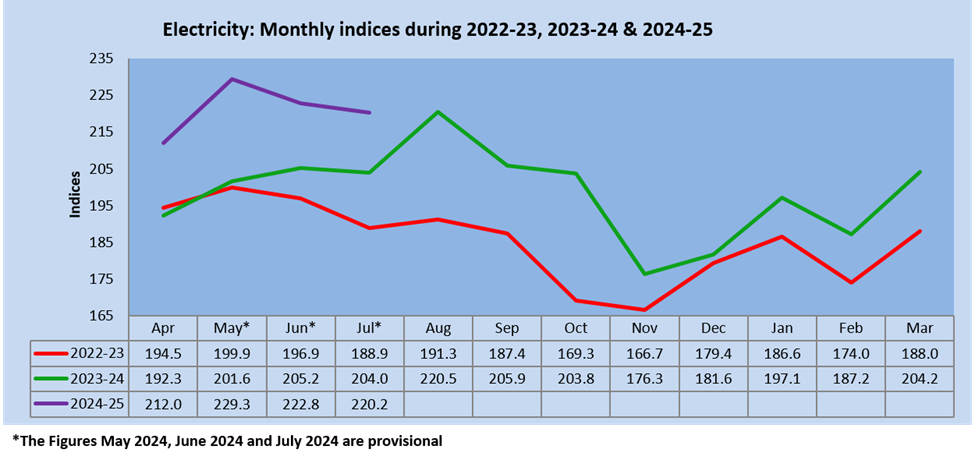
During summer, due to the scorching heat, the demand for air conditioners increases, and during occasions like Durga puja and Ganesh Chaturthi, the use of electricity increases. The government invests in green or renewable energy. The growth rate of Electricity in IIP growth for July 2024 is 7.9 per cent.
However, while the IIP growth in the electricity sector is good for India’s economic growth, it also has side effects. Most of India’s electricity generation is based on coal, petroleum, and natural gas. These are fossil fuels that emit carbon and many other pollutants. They damage India’s climate and air quality, particularly in urban areas. Burning fossil fuels releases greenhouse gasses like carbon dioxide, etc. These greenhouse gasses cause global warming and climate change. Fossil fuels are finite resources. Their massive extraction and consumption reduce the natural resources reserve. Most of the power plants in India are coal-fired power plants. The enormous amount of coal comes from mining massive areas, which leads to the displacement of the local population.
It also negatively impacts the environment, like water pollution, deforestation, biodiversity destruction, etc. Every power plant has massive machinery and equipment for boiling water, motors for turbines, etc. These machines need to be cool. The power plant uses water in a water-cooling process, and thermal power plants consume a massive amount of water. Due to the large amount of water used in power plants may lead to droughts in this region. India has many limitations in the electrical grid. India’s electric grids were built decades ago and based on old technology.
These equipment are insufficient for the recent electricity demand and are efficient enough to provide continuous current supply without any power cuts. The IIP growth in the electricity sector means the electricity sector gets more revenue or finance, but regular maintenance and upgrades are still delayed due to budget. Due to a lack of maintenance or upgrades, the electrical equipment is not efficient and reliable. The existing transmission lines are inadequate to manage the surge in demand for electricity. Providing renewable energy to consumers becomes very tough because it is produced in rural areas and lacks interconnection.
One of the main parts of renewable energy is storage technology. But in India storage technology like batteries are not developed at large scale, and existing batteries are not affordable. Due to a lack of clear and straightforward policy, new electric projects are delayed. Permitting processes and land conflicts are very complex government policies. The government earns more from people by taxation but invests very slowly in modernizing transition, grid and renewable energy. Due to all of these insufficiencies, the electricity sector faces infrastructure Bottlenecks. In rural areas, Electricity means frequent power cuts and voltage fluctuation when demand increases.
The government must invest more in modernizing grid technology. Smarter grid technology uses advanced sensors, automation, and real-time monitoring to help authorities understand and prevent bottlenecks. They should expand new transmission lines for higher flows and connect renewable energy. The government must also invest some budget in research and development of storage technology to reduce transmission congestion for renewable energy sources. The government must reform its policies and make them simple and easy. It must introduce new strict punishments if the environment is damaged. The government also introduced online portals for complaints to reduce bribe cases.
Growth in Overall
FAQ
What is the Index of Industrial Production or IIP?
The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is a key economic indicator showing various industrial sectors’ performance and growth.
What is the IIP growth rate in July 2024 in India?
According to the Ministry of Statistical Programme Implementation, the Index of Industrial Productiongrowth rate for July 202 is 4.8%.
What is the Index of Industrial Production growth rate for the three significant sectors?
The major sectors of IIP growth in India are Mining, Manufacturing, and electricity. Their growth rates for July 2024 are 3.7%, 4.6%, and 7.9%, respectively.
When was the IIP released?
The Index of Industrial Production estimates are released on the 12th of every month or the previous working day if the 12th is a holiday at 5.30 PM.
What is the base year for calculating IIP?
The current base year for the Index of Industrial Production is 2011-12. The base year is given a value of 100, and the IIP is a percentage increase or decrease from that.
What is the IIP comparison between July 2023 and July 2024?
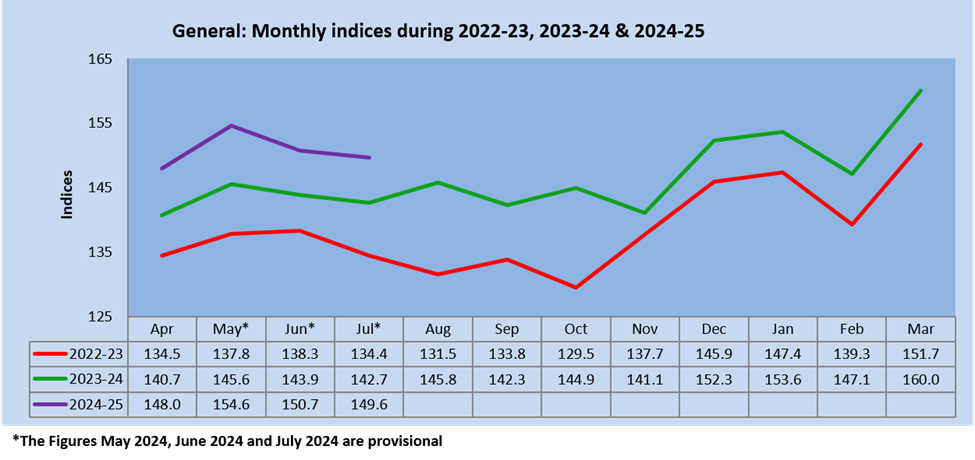
The Quick Estimates of IIP stands at 149.6 against 142.7 in July 2023. The Indices of Industrial Production for the Mining, Manufacturing and Electricity sectors for the month of July 2024 stand at 116.0, 148.6 and 220.2, respectively.


