History of Palmistry
Palmistry is often known as chiromancy, palm reading, or chirology. Palmistry aims to figure out an individual’s fortune by looking at the lines, shapes, and patterns on their palms. The primary origin of Palmistry is still unknown. However, it was also identified that Hindu sage Valmiki mentioned the ancient art of palm reading in his book “ The Teaching of Valmiki Maharshi on Male Palmistry.” several years ago. It indicates that Palmistry might have been introduced in India by the Hindu civilisation.
Culture and civilisation practices
Every civilisation and culture values the ancient art mentioned to understand their future path. Ancient Palmistry is mainly found in India, Arabian countries, Persia, Nepal, Sumer, China, and Babylonia. However, the art of Palmistry is a significant part of Indian astrology. The palm reader in India is called Jyotish; most people, especially youths, believe that the ancient palm Freudian art has the potential to highlight an individual’s past and future. These practices shape and define the identity, heritage, and evolution of societies across generations, fostering a sense of community and continuity. People in India firmly believe that the lines in the pal connect with the face of the universe.
Along with the Indians, it also observes the application of Palmistry to figure out the past and future of ancient China. The ancient chains Shengxiao (Chinese Zodiac) believe that the left hand’s palm lines represent the past and the right hand shows an individual’s future. Palmistry is also noticed in Greek and Roman history; they believe that the lines at the palm connect with the future and life path.
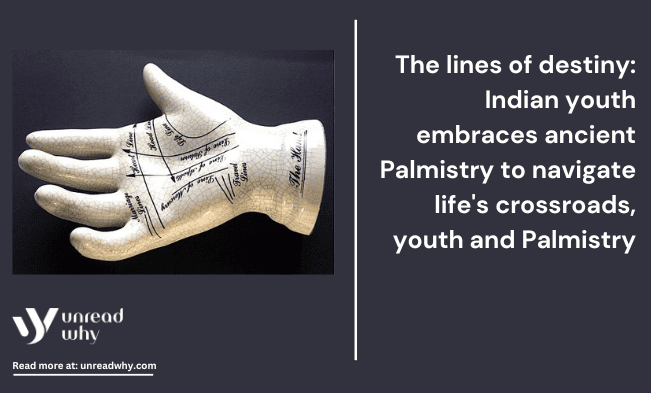
Palmistry is an ancient astrological practice. However, people, especially young people in the modern era, pay much attention to spiritual practices. Youth in the contemporary world believe that Palmistry has the potential to provide an understanding of an individual’s past and future path in their life. According to ancient history, an individual has seven crucial lines at hand. By examining the shape and position of those seven lines, astrologers can gain knowledge about what would take place in an individual’s life journey. The seven lines are a lifeline, table line, middle line, line of Venus, liver line, plain of Mars, and line of death altogether.
Youth and palmistry
However, most modern youths prioritise three lines: the death line, the heart line, and the middle or headline. The heart line is one of the most significant and famous lines among modern youth in India. The heart line is placed horizontally across the top of the palm, under the ring finger. The line demonstrates an individual’s emotional state, relationship situation and heart condition.
A more profound and bold heartline determines an individual’s stable emotional state and healthy relationship. The characteristics of the heart line gradually influence modern youth towards Palmistry. Youth in India want to know how their love life and heart condition will be in the future; therefore, the heart line is one of the topics most discussed among Indian youth.
The headline plays a significant role among modern people. The head is situated at the edge of the palm and runs horizontally across the middle of the palm. The head alone determines an individual’s resourcing ability and state. A long and unbroken headline indicates a good connection and the enhanced problem-solving ability of an individual. Lastly, the lifeline; people, especially youth in the modern era, consider the lifeline to be the most crucial palmistry line because it has the potential to highlight the life changes and general well-being of an individual. Mostly, the lifeline starts near the thumb and arcs downward toward the wrist.