Key Highlights:
- China pledges to cut economy-wide greenhouse gas emissions by 7-10% from peak levels by 2035, marking its first absolute reduction target
- The world’s largest carbon emitter plans to expand wind and solar capacity to 3,600 gigawatts, six times the 2020 levels
- China’s renewable energy sector already accounts for 56% of total installed capacity, with 373 million kilowatts added in 2024 alone
Opening Overview
China unveiled groundbreaking China climate goals during President Xi Jinping‘s virtual address to the United Nations Climate Summit on September 24, 2025, marking a pivotal moment in global climate action. The announcement represents the first time the world’s largest carbon polluter has committed to absolute emissions reductions, setting ambitious China climate goals that could reshape international environmental policy. As nations struggle to align with Paris Agreement targets, China’s comprehensive climate framework demonstrates unprecedented leadership in addressing global warming challenges. The significance of these commitments cannot be overstated, as global greenhouse gas emissions reached a record 57 gigatons of CO2 equivalent in 2023, requiring immediate action from all major economies.
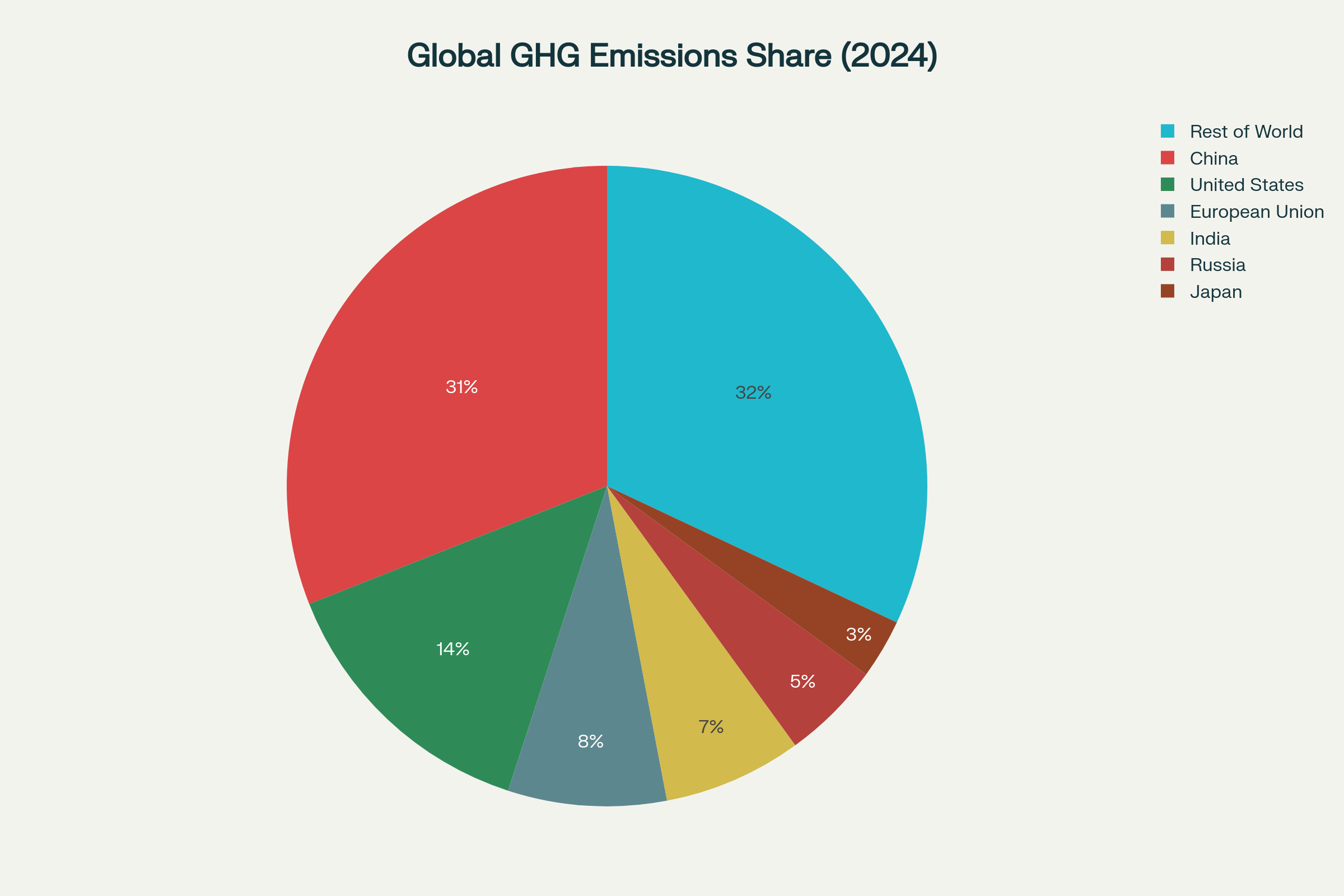
China accounts for nearly one-third of global greenhouse gas emissions, making its climate commitments crucial for global targets
China’s Ambitious Emissions Reduction Framework
Comprehensive Target Structure
- Reduce economy-wide net greenhouse gas emissions by 7-10% from peak levels by 2035, striving for better performance
- Increase non-fossil fuel share in energy consumption to over 30% by 2035
China’s newly announced China climate goals represent a fundamental shift from previous intensity-based targets to absolute emissions reductions, marking the nation’s commitment to join industrialized countries with declining emissions. The 7-10% reduction target from peak levels demonstrates China’s confidence in reaching emissions peak before 2030, potentially as early as 2025 according to climate analysts. These commitments build upon China’s track record of exceeding previous targets, including achieving its 1,200 GW renewable energy target six years ahead of schedule.
President Xi Jinping emphasized that these China climate goals represent China’s “best efforts” under the Paris Agreement requirements, requiring both domestic action and international cooperation. The framework includes expanding the National Carbon Emissions Trading Market to cover major high-emission sectors and establishing a climate-adaptive society by 2035.
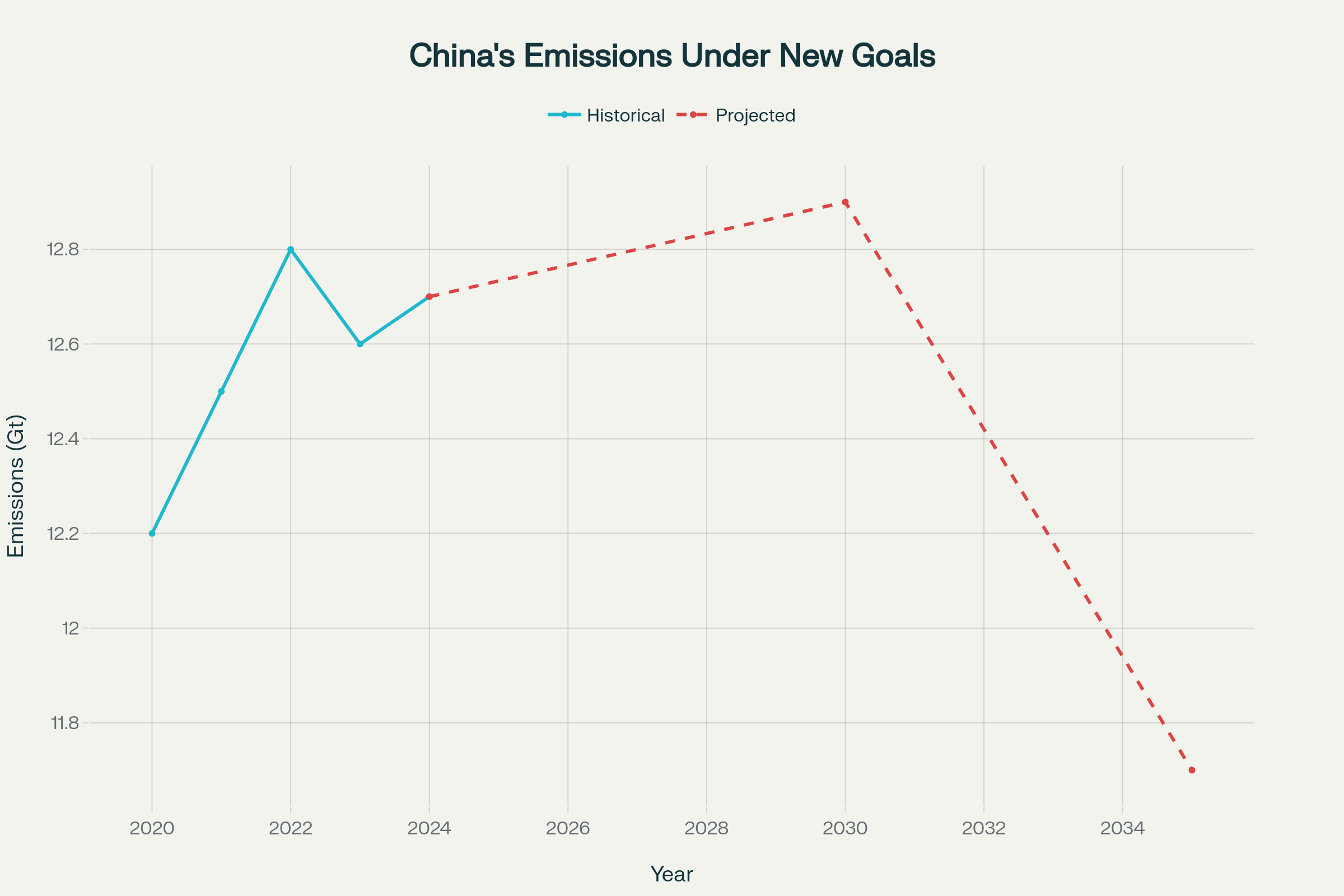
China’s emissions trajectory shows stabilization near peak levels with projected 7-10% reduction by 2035
Renewable Energy Expansion and Infrastructure Development
Record-Breaking Capacity Growth
- Wind and solar capacity to reach 3,600 gigawatts by 2035, representing over six-fold increase from 2020 levels
- Current renewable capacity already reached 1,889 billion kilowatts by end of 2024, comprising 56% of total installed capacity
China’s renewable energy achievements underscore the feasibility of its ambitious China climate goals, with the National Energy Administration reporting 373 million kilowatts of new renewable capacity added in 2024 alone. The country installed a record 277 gigawatts of solar power and 80 gigawatts of wind capacity in 2024, representing 45% and 18% growth respectively. These renewable expansion targets appear conservative given current deployment rates, with analysts noting that meeting the 3,600 GW target requires less than 200 GW annual additions compared to 360 GW added in 2024.
Combined wind and solar generation reached 1.83 trillion kilowatt-hours in 2024, equivalent to the electricity consumption of China’s entire tertiary industry. The renewable energy sector contributed over 10% of China’s GDP for the first time in 2024, with combined investment and sales reaching $1.9 trillion, creating economic incentives that support China climate goals implementation.
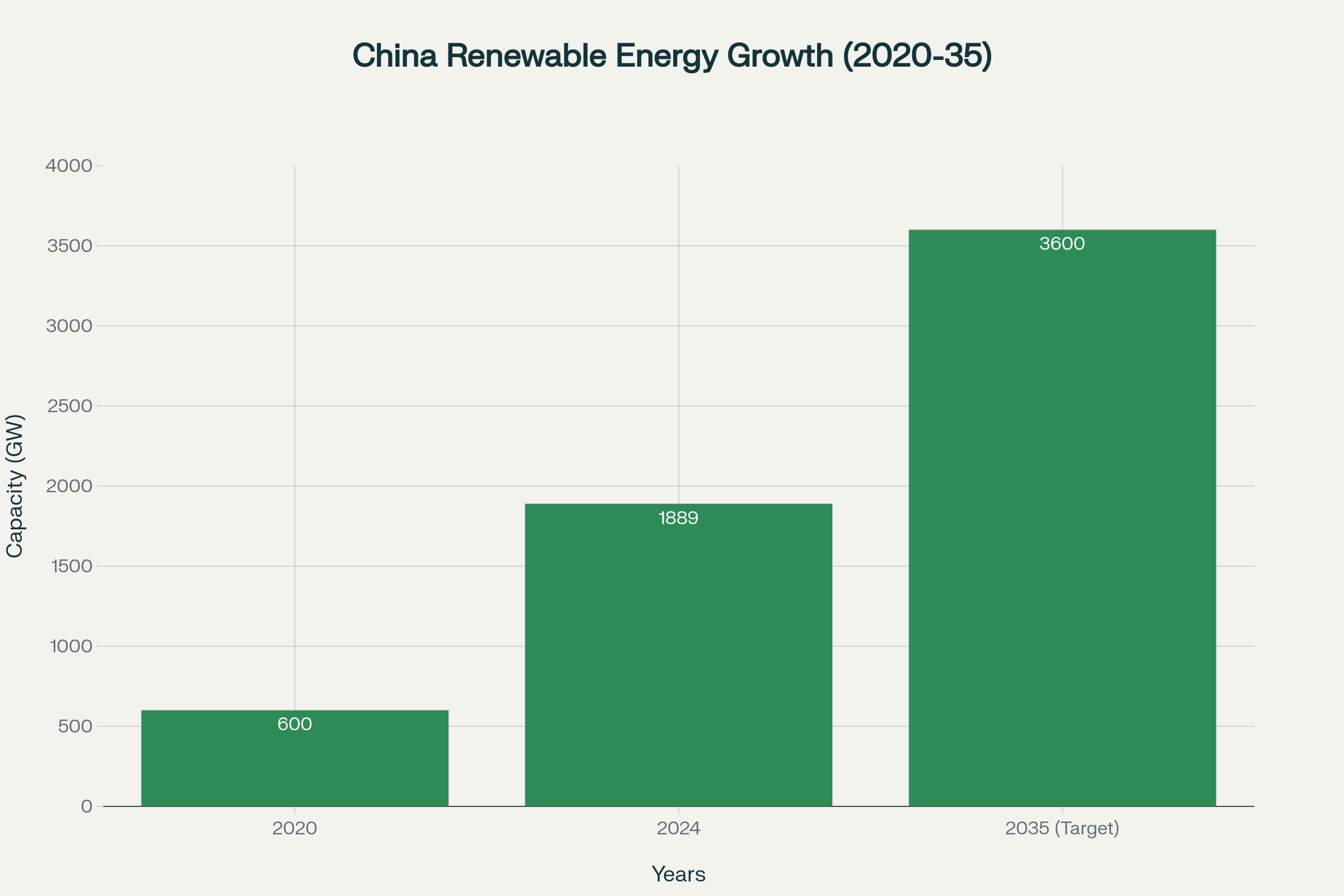
China’s renewable energy capacity has nearly tripled since 2020 and is projected to reach 3,600 GW by 2035
Global Impact and International Context
China’s Emissions Leadership Position
- China accounts for approximately 30-35% of global greenhouse gas emissions, making it the world’s largest current emitter
- Despite high current emissions, China’s cumulative historical emissions remain lower than the United States and European Union
China’s China climate goals carry enormous global significance given the country’s position as the world’s largest carbon emitter, responsible for over 12.6 gigatons of CO2 equivalent emissions in 2023. The timing of these commitments contrasts sharply with the United States’ withdrawal from the Paris Agreement under President Trump, who dismissed climate change as a “con job” during his UN address. China’s emissions have stabilized near record-high levels in 2024, with projections suggesting the country may have already reached peak emissions or will do so by 2025.
These China climate goals address criticism about China’s historical approach of setting intensity-based targets rather than absolute reductions, aligning the country with international best practices. President Xi emphasized the need for developed countries to lead climate action while supporting developing nations, calling for fair burden-sharing in global climate efforts.
Economic and Technological Transformation Targets
Clean Technology Market Leadership
- New energy vehicles to become mainstream in car sales by 2035
- Forest stock volume expansion to over 24 billion cubic meters
China’s China climate goals extend beyond emissions reductions to encompass comprehensive economic transformation, with new energy vehicles positioned to dominate the domestic automotive market. The country already leads global clean technology manufacturing, producing 92% of the world’s solar modules and 82% of wind turbines, positioning it well to achieve these targets. China’s carbon intensity decreased by 3.4% in 2024, though falling short of the 3.9% target, highlighting implementation challenges that must be addressed. The nation’s commitment to expanding forest coverage aligns with nature-based solutions for carbon sequestration, complementing technological approaches within the broader framework. These sectoral transformation goals reflect China’s strategy of leveraging its manufacturing advantages to accelerate global clean technology deployment while achieving domestic climate objectives.
Closing Assessment
China’s announcement of comprehensive China climate goals represents a watershed moment in global climate governance, demonstrating how the world’s largest emitter can transition from growth-focused to sustainability-oriented development pathways. The 7-10% absolute emissions reduction target, combined with massive renewable energy expansion plans, positions China as a leader in climate action despite ongoing geopolitical tensions. These commitments gain credibility from China’s track record of exceeding previous climate targets and its dominant position in clean technology manufacturing. As the international community prepares for COP30 in Brazil, China’s ambitious China climate goals may pressure other major emitters to strengthen their own commitments and accelerate the global transition to net-zero emissions.


