Key Highlights
- A 10-foot wide road collapse occurred in Delhi’s Janakpuri area on September 2, 2025, due to waterlogging from heavy rainfall, requiring immediate area barricading
- Technical teams from MCD and Delhi Jal Board were deployed to assess damage and initiate repairs on Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes incident
- The collapse reflects broader infrastructure challenges as Delhi experienced its wettest August in 15 years with 72% excess rainfall
Opening Overview
Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes the capital’s deteriorating infrastructure vulnerabilities as a significant road cave-in incident occurred on September 2, 2025, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive urban planning reforms. What began as a small hole in the roadway due to waterlogging from heavy rainfall quickly expanded to a dangerous 10-foot wide cavity, forcing authorities to barricade the affected stretch and halt traffic movement. This latest example of how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes infrastructure deficiencies represents a concerning pattern of failures across the capital during the current monsoon period.
The collapse occurred on a Tuesday evening when intense rainfall led to severe waterlogging, compromising the road’s structural integrity. Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) officials, along with Delhi Jal Board (DJB) technical teams, responded swiftly to assess the damage and initiate emergency repairs. Fortunately, no injuries were reported in this incident where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes serious municipal preparedness gaps, though the traffic disruptions significantly impacted local commuters and residents.
This latest infrastructure failure comes amid what meteorological data confirms as Delhi’s wettest August in over a decade, with the city recording 399.8 mm of rainfall during the month. Such extreme precipitation events continue to reveal how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes the inadequacies in the city’s drainage systems and road construction quality, making such incidents increasingly common during monsoon periods.
Infrastructure Vulnerability During Extreme Weather Events
- Delhi recorded its wettest August in 15 years with 399.8 mm of rainfall, representing a 72% excess over normal precipitation levels
- The city has experienced four major storm events in recent months, with May 2025 marking the wettest May since 1901 with 186.4 mm of rainfall
The incident where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes infrastructure crisis illustrates the broader vulnerabilities facing the capital during periods of intense rainfall. According to official meteorological data, Delhi has experienced unprecedented precipitation patterns throughout 2025, with August recording 399.8 mm of rainfall compared to the normal average. This excessive rainfall has consistently overwhelmed the city’s drainage infrastructure, leading to widespread waterlogging and subsequent road failures that demonstrate how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes systematic problems.
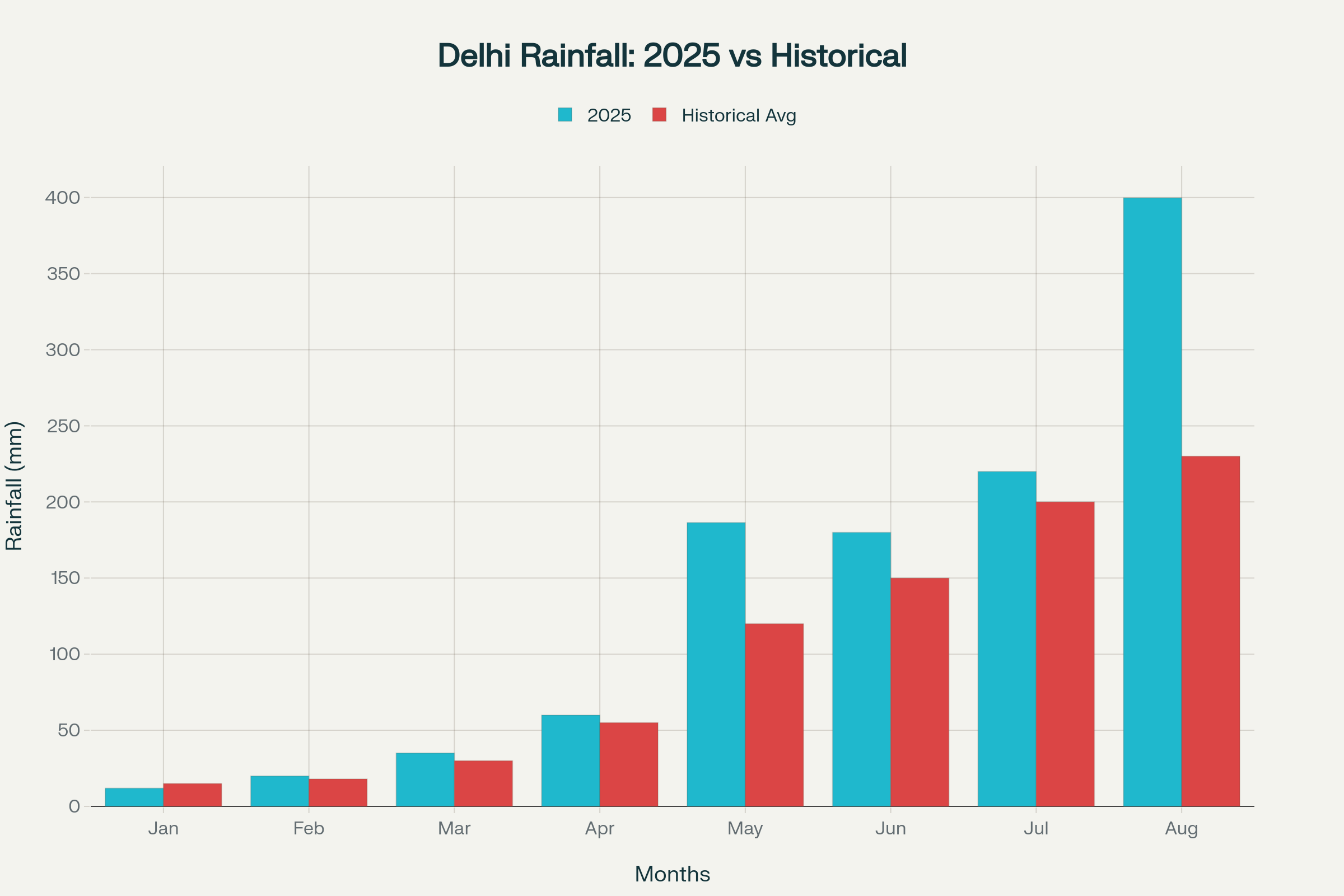
Delhi’s Monthly Rainfall in 2025 Compared to Historical Averages (Jan-Aug)
| Month | 2025 Rainfall (mm) | Historical Average (mm) | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 12 | 15 | -3 mm |
| February | 20 | 18 | +2 mm |
| March | 35 | 30 | +5 mm |
| April | 60 | 55 | +5 mm |
| May | 186.4 | 120 | +66.4 mm |
| June | 180 | 150 | +30 mm |
| July | 220 | 200 | +20 mm |
| August | 399.8 | 230 | +169.8 mm |
Delhi’s road network spans approximately 18,000 kilometers, with the Municipal Corporation of Delhi responsible for maintaining 15,000 kilometers of internal roads. However, the quality of road construction and maintenance has come under scrutiny, particularly as incidents where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes fundamental weaknesses in the infrastructure become more frequent. The city’s limited working period for road repairs, typically restricted to about five months annually due to weather constraints, further compounds these challenges.
The technical response to how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes infrastructure gaps involved immediate deployment of MCD and DJB teams, reflecting established protocols for infrastructure emergencies. However, the rapid expansion of what initially appeared as a small hole to a 10-foot wide cavity within hours demonstrates the severity of structural vulnerabilities when roads are exposed to waterlogging conditions. Such incidents raise critical questions about the long-term durability and design standards of Delhi’s road infrastructure.
Weather patterns contributing to events where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes infrastructure weaknesses have shown increasing intensity and frequency. The India Meteorological Department has documented how climate variations, including frequent western disturbances and cyclonic circulations, have contributed to these extreme precipitation events that compromise urban infrastructure stability.
Municipal Response and Drainage System Performance
- PWD completed desilting of 1,892 kilometers out of Delhi’s 2,158 kilometers of maintained drains by July 2025, achieving an 88.5% completion rate
- MCD cleared 170,620 tonnes of silt from drains between January and June 2025, surpassing its target of 126,474 tonnes
The municipal response to how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes systemic issues highlighted both the preparedness and limitations of Delhi’s civic infrastructure management. Technical teams from the Municipal Corporation of Delhi and Delhi Jal Board were immediately dispatched to assess the damage and implement safety measures. The swift barricading of the affected area prevented potential accidents, though the incident where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes underlying problems revealed drainage and road construction quality issues that contribute to such failures.
Delhi’s drainage system performance has been a critical factor in preventing or exacerbating road failures like the situation where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes infrastructure vulnerabilities. According to official progress reports, the Public Works Department had completed desilting of 1,892 kilometers of drains by July 2025, representing 88.5% of the target. However, zone-wise disparities remain significant, with west Delhi showing the largest gaps in completion rates. This incomplete drainage maintenance directly contributes to waterlogging conditions that lead to infrastructure failures similar to how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes systematic deficiencies.
| Drainage Maintenance Statistics | Target | Achieved | Completion Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Drain Length (km) | 2,158 | 1,892 | 88.5% |
| Silt Cleared (tonnes) | 126,474 | 170,620 | 134.9% |
| Waterlogging Points Identified | – | 445 | – |
| Major Roads Maintained (km) | – | 1,449 | – |
The Municipal Corporation of Delhi has implemented various measures to address infrastructure vulnerabilities, including the deployment of 52 mechanical road sweepers across the 1,400-kilometer arterial road network. Additionally, 30 mobile anti-smog guns and water sprinklers have been deployed to manage dust and maintain road conditions. However, these preventive measures have proven insufficient to prevent critical failures like the instance where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes infrastructure gaps when extreme weather events occur.
Emergency response protocols demonstrated during the incident where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes response capabilities reflect established procedures for infrastructure emergencies. Police teams responded immediately upon receiving information about the road collapse, implementing traffic diversions and ensuring public safety. The coordination between MCD, DJB, and police authorities shows functional emergency management systems, though the frequency of such incidents suggests the need for more robust preventive infrastructure planning.
Traffic Management and Economic Impact Assessment
- Delhi’s PWD maintains 1,449 kilometers of major roads that handle approximately 70% of the city’s total traffic volume
- The city has identified 445 waterlogging points that pose recurring risks to traffic movement during monsoon periods
The traffic disruptions caused by the situation where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes mobility challenges reflect broader transportation issues facing Delhi during monsoon periods. The affected stretch required complete closure to vehicular movement, forcing authorities to implement traffic diversions that impacted thousands of daily commuters. Such incidents demonstrate how individual infrastructure failures like the case where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes systemic problems can cascade into city-wide traffic management crises.
Economic implications of incidents where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes infrastructure deficiencies extend beyond immediate repair costs to include productivity losses from traffic disruptions. Delhi’s Public Works Department maintains 1,449 kilometers of major roads that carry 70% of the city’s traffic, making any significant road closure highly disruptive to economic activity. The example of how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes economic vulnerabilities represents just one of numerous infrastructure failures that collectively impose substantial costs on the capital’s residents and businesses.
Traffic management during the incident where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes coordination challenges required immediate cooperation between multiple agencies to ensure public safety and maintain traffic flow on alternative routes. Delhi Traffic Police issued advisories warning commuters to avoid the affected area while repair work was initiated. Such responses have become routine during monsoon periods when situations like Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes infrastructure weaknesses occur with increasing frequency across the city.
The financial burden of addressing infrastructure failures such as the case where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes budget constraints falls primarily on municipal budgets already strained by ongoing maintenance requirements. MCD has allocated resources for emergency repairs and preventive measures, including the acquisition of 3,200 stacks of cold mix bitumen emulsion for road maintenance. However, the recurring nature of incidents where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes systematic issues suggests the need for more comprehensive infrastructure investment and planning approaches.
Long-term traffic planning must account for the increasing frequency of weather-related infrastructure failures like the situation where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes planning deficiencies. As climate patterns continue to intensify, Delhi’s transportation network requires enhanced resilience measures to minimize the impact of such incidents on urban mobility and economic activity.
Engineering Solutions and Future Infrastructure Planning
- MCD has initiated repair work using 3,200 stacks of cold mix bitumen emulsion, with each stack containing 32 kilograms of material suitable for wet road conditions
- Delhi government implemented a weekly action plan requiring road maintenance agencies to repair at least one road per zone every Saturday
The engineering response to how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes technical challenges has involved both immediate remedial measures and longer-term infrastructure planning considerations. The use of cold mix bitumen emulsion for repairs represents an adaptation to Delhi’s challenging weather conditions, as this material functions effectively on wet roads unlike traditional hot bitumen that performs poorly during monsoon periods. However, the durability of such patches remains questionable, as evidenced by recurring failures that demonstrate how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes engineering limitations.
Technical assessment of the incident where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes structural weaknesses revealed the rapid progression from a small surface defect to a major failure spanning 10 feet in width. This rapid deterioration pattern suggests underlying issues with road base construction and drainage integration that extend beyond surface-level maintenance concerns. Engineering teams must address these fundamental design flaws to prevent future occurrences similar to how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes infrastructure vulnerabilities.
Municipal engineering departments have responded to incidents where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes maintenance gaps by implementing systematic maintenance protocols. The Delhi government’s weekly action plan requires each civic agency to undertake repairs of at least one road per zone every Saturday. This proactive approach aims to identify and address potential failure points before they develop into major incidents such as the case where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes critical infrastructure problems.
Advanced engineering solutions being considered for Delhi’s road network include improved drainage integration, enhanced base construction materials, and better waterproofing techniques. These measures specifically target the conditions that contributed to situations where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes infrastructure deficiencies and similar failures. However, implementation requires significant capital investment and coordinated planning across multiple civic agencies.
Quality control measures have been enhanced following incidents where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes oversight gaps, with increased supervision of contractor work and materials specifications. The engineering department now requires detailed documentation of repair procedures and materials used, ensuring accountability in infrastructure maintenance. These protocols aim to prevent the conditions that led to how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes systematic problems from recurring in other areas of the city.
Closing Assessment
The incident where Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes infrastructure vulnerabilities serves as a stark reminder of the capital’s challenges during extreme weather events. While immediate response protocols functioned effectively, preventing casualties and managing traffic disruption, the underlying causes of such failures demand comprehensive attention. The combination of record-breaking rainfall, incomplete drainage maintenance, and aging road infrastructure created the conditions that led to this significant collapse.
Moving forward, Delhi’s approach to infrastructure resilience must evolve beyond reactive maintenance to proactive planning that anticipates extreme weather impacts. How Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes current inadequacies demonstrates that existing engineering standards and maintenance practices are insufficient for the city’s changing climatic conditions. Investment in robust drainage systems, improved construction materials, and enhanced quality control measures will be essential to prevent similar incidents.
The broader implications of how Delhi’s Janakpuri Road Collapse Exposes planning deficiencies extend to urban development and climate adaptation strategies. As Delhi continues to experience unprecedented weather patterns, infrastructure design must incorporate greater resilience factors and emergency response capabilities. The lessons learned from this incident should inform future road construction projects and maintenance protocols across the capital, ensuring that Delhi’s transportation network can withstand the challenges of an increasingly unpredictable climate.


