Key Highlights
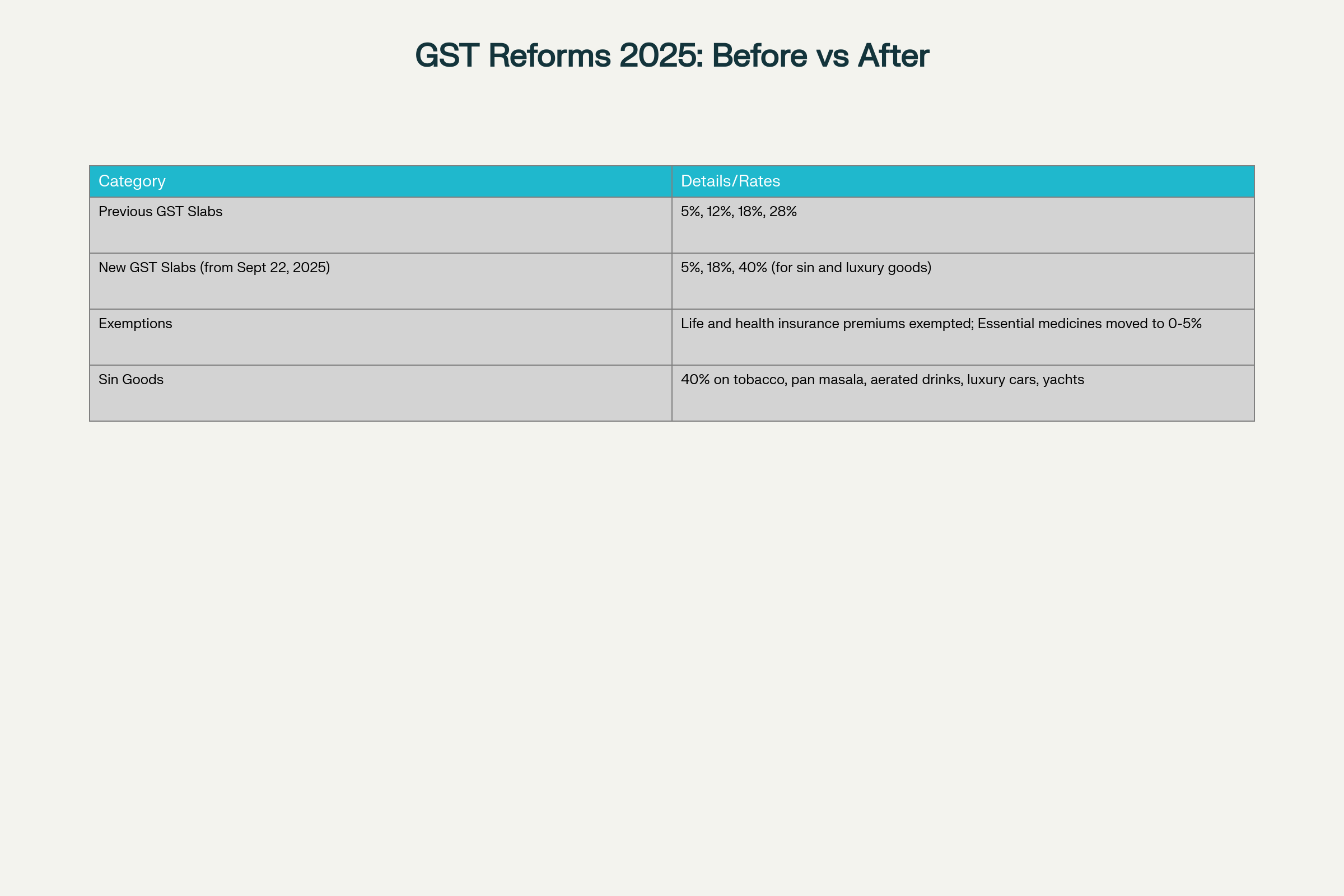
- Two-slab GST structure: Finance Minister confirms 18-month preparation period for reducing GST slabs to 5% and 18% with exemptions for health and life insurance premiums
- Revenue impact: GST slab reduction expected to cause ₹48,000 crore revenue loss while state governments prepare for significant shortfalls across multiple sectors
- Implementation timeline: New GST structure effective September 22, 2025, with unanimous GST Council approval despite state revenue concerns
Opening Overview
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman’s revelation about the 18-month development process behind India’s landmark GST slab reduction reforms provides crucial insight into one of the country’s most significant tax overhauls since independence. Speaking at an NDTV summit, Sitharaman emphasized that the comprehensive GST slab reduction initiative was not a reactive measure to Donald Trump’s proposed tariffs but a carefully planned restructuring aimed at providing relief to the common man.
The GST reduction from four tiers to a simplified two-tier structure represents a fundamental shift in India’s indirect taxation framework, with far-reaching implications for consumers, businesses, and state revenues. This transformation of the GST reduction system demonstrates the government’s commitment to making taxation more transparent and accessible while addressing the needs of middle-class taxpayers and small businesses across the nation.
HTML preview is not yet fully accessible. Please switch screen reader to virtualized mode to navigate the below iFrame.
A truly historic reform for New India! 🙏
— Devendra Fadnavis (@Dev_Fadnavis) September 3, 2025
Under the visionary leadership of Hon. PM Narendra Modi Ji and the dedicated efforts of Hon Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman ji, GST has been simplified forever.
By abolishing 12% & 28% slabs, and moving to just 5% & 18%, a burden on… pic.twitter.com/eM3EuxRkpd
Political Genesis and Strategic Planning Behind GST Slab Reduction
The journey toward GST reduction began with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s directive to provide meaningful relief to the ‘aam aadmi’ during discussions preceding the Union Budget presentation. Sitharaman revealed that the conceptualization of GST reduction reforms started even before her eighth consecutive budget delivery, when she introduced middle-class tax rebates for salaried individuals earning up to ₹12 lakh annually.
Key development milestones for the GST reduction included:
- Extended planning period: The Finance Minister required substantial time to develop a comprehensive reform package worthy of presentation to the Prime Minister
- Strategic timing: Sitharaman approached PM Modi with detailed GST reduction proposals only in May 2025, highlighting the meticulous preparation involved
The GST reduction initiative gained momentum following the Prime Minister’s Independence Day announcement promising “Next-Generation GST reforms” as a “Diwali gift” for citizens. This political commitment to GST reduction reflected the government’s recognition of mounting pressure on household budgets and the need for structural tax reforms to stimulate economic growth.
The strategic approach to GST reduction emphasized consensus-building with state governments, recognizing their crucial role in India’s federal tax structure. The Finance Minister’s careful coordination ensured that the GST reduction proposals addressed both central government objectives and state revenue concerns.
Revenue Implications and State Government Concerns About GST Reduction
The GST reduction reforms present significant fiscal challenges for state governments across India, with revenue projections indicating substantial shortfalls in the immediate term. Multiple opposition-ruled states have expressed concerns about the financial impact of GST reduction on their budgetary allocations for welfare schemes and development programs.
State-wise revenue impact projections from GST reduction include:
- Karnataka: Estimated annual loss of ₹15,000 crore from GST reduction implementation
- Kerala: Projected shortfall of ₹8,000-10,000 crore due to GST reduction measures
- Punjab: Anticipated revenue loss exceeding ₹4,000 crore from GST reduction
- Jharkhand: Expected impact of approximately ₹2,000 crore from GST reduction reforms
The Centre has estimated the net revenue implication of GST reduction at ₹48,000 crore, which officials describe as “fiscally sustainable” given expected consumption growth. However, state finance ministers have coordinated their response to GST reduction, arguing that immediate fiscal pressures could undermine funding for critical areas including health, education, and social welfare programs.
Sitharaman addressed state concerns about GST reduction by highlighting the absence of compensation mechanisms since 2022, when the GST Compensation Cess structure was modified. The current cess collection framework prioritizes repaying COVID-related loans rather than offsetting state revenue losses from GST slab reduction measures. The Finance Minister suggested that improved collection efficiency rather than higher rates represents the optimal path forward for maintaining revenue stability amid GST slab reduction implementation.
Comprehensive Sectoral Impact of GST Reduction Implementation
The GST reduction reforms encompass sweeping rate modifications across multiple economic sectors, fundamentally altering the tax burden on consumers and businesses. The transition from a four-tier system to the simplified GST reduction structure affects household essentials, automobiles, healthcare, and luxury goods through targeted rate adjustments.
Healthcare and insurance sectors benefit significantly from GST reduction measures:
- Insurance exemptions: Life and health insurance premiums now completely exempt from GST under the slab reduction framework
- Medicine accessibility: 33 life-saving drugs moved from 12% to zero percent through GST reduction
- Medical equipment: Thermometers, glucometers, and diagnostic kits reduced from 12-18% to 5% under GST slab reduction
Consumer goods experience substantial relief through GST reduction implementation, with household essentials including soaps, toothpaste, and Indian breads either exempted or moved to the 5% tier. The automobile sector sees comprehensive rate reductions under GST reduction, with small cars and two-wheelers below 350cc moving from 28% to 18%.
The GST slab reduction framework introduces a 40% levy on luxury and sin goods, including tobacco, pan masala, aerated drinks, and high-end vehicles. This targeted approach ensures revenue generation from non-essential consumption while providing relief for basic necessities through GST slab reduction measures. Agricultural sector benefits include reduced rates on tractors, farm machinery, and irrigation equipment, supporting the government’s rural development priorities through GST slab reduction implementation.
Economic Strategy and Long-term Vision for GST Slab Reduction Success
The GST slab reduction initiative represents a strategic economic approach designed to stimulate domestic consumption while maintaining revenue sustainability through improved compliance mechanisms. Sitharaman emphasized that GST slab reduction reforms create a virtuous cycle where lower tax rates generate higher demand, expanded tax base, and ultimately stronger revenue collections.
Economic benefits projected from GST slab reduction include:
- Enhanced affordability: Lower tax burden on essential goods increases household purchasing power through GST slab reduction
- Manufacturing competitiveness: Corrected inverted duty structures boost domestic value addition under GST slab reduction framework
- MSME support: Reduced input costs for small businesses through comprehensive GST slab reduction measures
- Compliance improvement: Simplified two-tier structure reduces disputes and encourages voluntary compliance with GST slab reduction
The GST slab reduction timeline ensures implementation by September 22, 2025, coinciding with Navratri festivities to maximize consumer benefit during the festive season. Industry associations have welcomed GST slab reduction as “pathbreaking” and “compliance-easing,” highlighting reduced administrative burden for businesses.
The Finance Minister’s emphasis on “ease of living” through GST slab reduction reflects broader governance objectives of simplifying citizen-government interactions. This approach positions GST slab reduction as both an economic reform and administrative efficiency measure, supporting India’s transition toward a more streamlined tax architecture. The success of GST slab reduction will depend on achieving the delicate balance between immediate revenue concerns and long-term growth objectives through sustained economic momentum and improved tax compliance.
Final Perspective on GST Slab Reduction Transformation
The GST slab reduction reforms announced by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman represent a culmination of extensive planning and strategic coordination that prioritizes citizen welfare while addressing structural inefficiencies in India’s indirect tax system. The 18-month development period for GST slab reduction demonstrates the government’s commitment to thorough preparation rather than hasty policy implementation, ensuring that the simplified two-tier structure addresses both immediate relief needs and long-term economic objectives.
The unanimous GST Council approval of GST slab reduction measures, despite initial state revenue concerns, reflects successful federal coordination and shared vision for India’s tax modernization. While states face immediate fiscal challenges from GST slab reduction implementation, the reforms’ emphasis on consumption stimulation and compliance improvement offers a pathway toward sustainable revenue growth.
The GST slab reduction initiative’s focus on essential goods, healthcare accessibility, and MSME support aligns with broader economic democratization goals while maintaining targeted taxation on luxury consumption. As India approaches the September 22, 2025 implementation date, the success of GST slab reduction will be measured not only by revenue metrics but by its impact on household affordability, business competitiveness, and overall economic inclusivity. This transformation marks a significant milestone in India’s ongoing tax reform journey, positioning GST slab reduction as a model for balancing fiscal responsibility with citizen-centric governance.


