Key Highlights
- GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution restrictions triggered by AQI surging above 400 in Delhi-NCR.
- Schools up to Class 5 in Delhi mandated to conduct classes in hybrid mode to protect students against GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution.
- Stringent bans placed on construction, vehicle emissions, and several industrial activities as part of GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution emergency measures.
Opening Overview
Escalating GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution in the capital has compelled authorities to impose strict emergency measures under Stage III of the Graded Response Action Plan. Triggered by a sudden spike in AQI from ‘very poor’ to ‘severe’, with readings consistently above 420, these restrictions are pivotal to combat dangerous smog engulfing the National Capital Region. One of the key measures taken under the GRAP-3 protocol is the transition of schools up to Class 5 to hybrid mode, providing a shield for young children who are most vulnerable to hazardous air quality.
The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM), responsible for enforcing policies addressing GRAP-3 Air Pollution, has emphasized a holistic approach that includes bans on dust-generating construction, older polluting vehicles, and several industrial processes. The implementation of GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution measures underscores both the severity of this crisis and the authorities’ priority to limit further environmental decline. The article explores how the GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution framework impacts daily urban life, while calling attention to the urgent need for sustainable solutions and improved environmental governance.
Stringent Restrictions Under GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution
GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution represents the most severe tier of emergency response to deteriorating air quality in Delhi and adjacent NCR zones. Authorities have suspended all non-essential construction activities—earthwork, piling, painting, masonry, and tiling—to significantly cut down particulate emissions. The closure of stone crushers, mining, and hot-mix plants further reflects GRAP-3 Air Pollution policy. Only projects deemed essential, like sanitation and healthcare, can continue under strict norms.
Vehicle emissions—another major driver—are addressed by restricting BS III petrol and BS IV diesel vehicles across Delhi-NCR roads. This measure ensures only electric, CNG, or upgraded BS VI diesel vehicles operate, reducing dangerous nitrogen oxide and particulate levels under the GRAP-3 plan. Additionally, mechanized road sweeping and water sprinkling have been intensified to control dust, and public transport is being promoted through differential fares.
GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution restrictions extend to other sectors, such as targeted closures of pollution-heavy industries and advisories for private companies to switch to hybrid work models, reflecting a coordinated enforcement designed to meaningfully lower emissions and protect health during the air quality crisis.
Education Policy Shift: Hybrid Mode to Safeguard Children
Children are most susceptible to the effects of Air Pollution due to developing lungs and higher respiration rates. In response, the Directorate of Education has mandated that schools up to Class 5 shift to hybrid teaching formats under the GRAP-3 policy. This approach allows parents to favour online instruction, minimizing physical attendance and reducing exposure risks. The policy applies uniformly to all schools to ensure broad protection as part of the GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution intervention.
Recent health studies linked to GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution reveal that prolonged exposure can cause irreversible lung damage, raise the risk of allergies, and suppress immunity. The hybrid school directive under GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution aims to maintain educational continuity while minimizing health risks for children. School administrators are required to ensure swift communication of these changes to parents and the rapid implementation of online platforms so students do not suffer learning loss during the GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution crisis.
दिल्ली में वायु गुणवत्ता की स्थिति को देखते हुए CAQM द्वारा GRAP-III (ग्रैप-3) लागू किया गया है।
— Rekha Gupta (@gupta_rekha) November 11, 2025
हमारी सरकार प्रदूषण नियंत्रण को लेकर पूरी गंभीरता और तत्परता के साथ कार्य कर रही है।
कल से स्कूलों में पांचवीं कक्षा तक की पढ़ाई हाइब्रिड मोड में संचालित होगी। शहर के सभी हॉटस्पॉट… pic.twitter.com/kxf4sXcBXr
Health Impact: GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution and Public Awareness
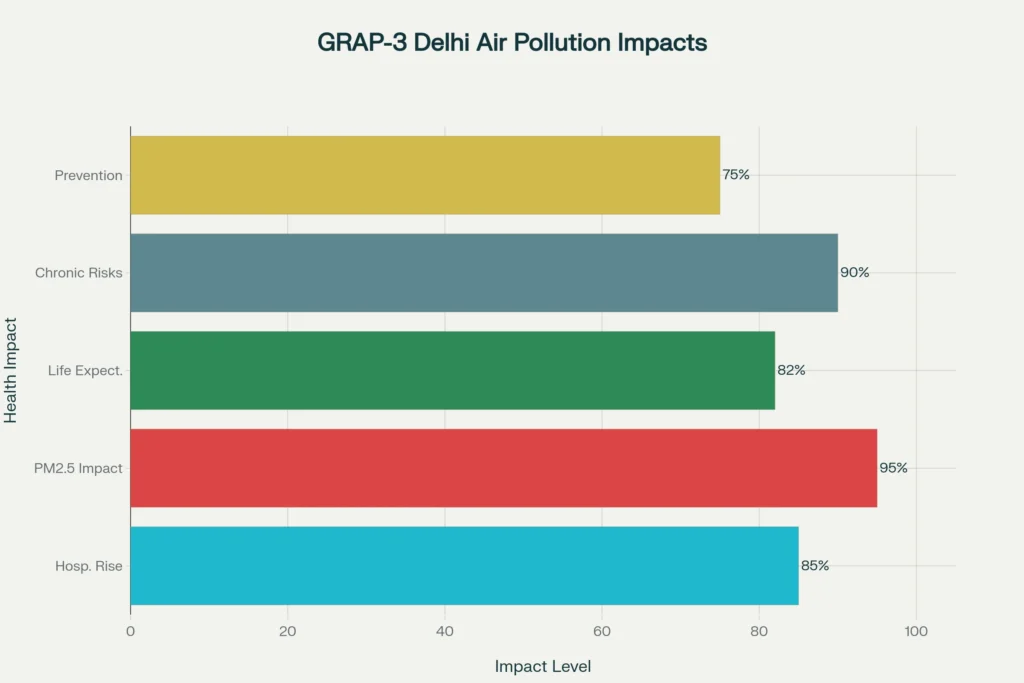
The implementation of GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution is driven by health findings showing its direct connection to increased hospitalizations for asthma, bronchitis, and cardiac ailments. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and toxic gases generated during its peaks penetrate deep into the lungs and bloodstream, causing widespread inflammation. The Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) documents substantial reductions in life expectancy—by an average of 8.2 years for Delhi-NCR residents exposed to consistent Delhi Air Pollution.
Medical experts warn that chronic effects of GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution include lifelong respiratory complaints, developmental delays in children, and elevated cancer risks. The public has been advised to limit outdoor activities, use air purifiers and certified masks, and immediately report symptoms linked to GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution. Such awareness efforts are essential to the overall health strategy as restrictions alone cannot fully mitigate the impacts of GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution without community engagement.
Governance and Policy: GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution Framework
The GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution protocol forms part of a graded emergency framework, developed to preempt and control rising air pollution with escalating policy actions. GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution Stage III is activated whenever AQI exceeds 400, with bans and advisories spanning construction, vehicles, and educational practices. CAQM, DPCC, and municipal bodies are responsible for the execution and monitoring of Delhi Air Pollution measures.
November 2025’s spike in GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution marked the most hazardous levels since records began, prompting rapid activation of all emergency controls. The efficacy of Air Pollution measures depends on strict compliance, real-time monitoring, and public participation. Authorities continue to refine the Air Pollution system, integrating new technologies and data for more timely, effective interventions.
Final Perspective
As Delhi contends with the ravages of GRAP-3 Delhi Air Pollution, multipronged government action provides essential protection for children and public health. The switch to hybrid schooling, construction bans, and vehicular restrictions echo the seriousness of Delhi Air Pollution response, while also highlighting broader lessons on urban planning and sustainable development. Continued vigilance, community participation, and long-term reforms remain vital as Delhi and the NCR seek to overcome Air Pollution threats.


