Key Highlights:
- A 27-year-old man drowned in floodwaters at Balkampet underpass, marking the fourth death this week in Hyderabad flooding incidents
- Telangana recorded exceptional rainfall with Amberpet receiving 145.8mm in 24 hours, the highest in the state on September 18, 2025
- Three people remain missing from separate flood incidents, with search operations ongoing by HYDRAA teams across multiple locations
Opening Overview
Hyderabad floods have claimed another life as relentless monsoon rains continue to devastate Telangana, with Mohammed Sharfuddin becoming the fourth fatality this week after being swept away by floodwaters near New Balkampet Bridge. The 27-year-old was returning home from work on his motorcycle Wednesday night when the tragic incident occurred, highlighting the growing crisis of Hyderabad floods that have overwhelmed the city’s drainage infrastructure. Despite wearing protective gear including a helmet and raincoat, Sharfuddin could not escape the powerful currents that have transformed city streets into dangerous waterways during this latest spell of extreme weather.

The devastating impact of Hyderabad floods extends beyond individual tragedies, with official meteorological data revealing unprecedented rainfall intensity across the region. According to the India Meteorological Department‘s latest district-wise rainfall report dated September 18, 2025, Amberpet recorded the highest rainfall in Telangana at 145.8mm in 24 hours, followed by multiple Hyderabad locations exceeding 100mm. This exceptional precipitation has created conditions where Hyderabad floods have become a recurring nightmare for residents, with three separate incidents this week alone resulting in missing persons and confirmed fatalities.mausam.
Unprecedented Rainfall Intensity Triggers Widespread Flooding
The current wave of Hyderabad floods stems from extraordinary meteorological conditions that have brought the heaviest rainfall in five years to the region. Data from the Telangana Development Planning Society reveals that multiple areas within Hyderabad recorded rainfall exceeding 140mm on September 17-18, with Musheerabad reporting a staggering 184.3mm during the peak intensity period. This volume represents nearly three times the city’s drainage capacity, which was originally designed to handle approximately 2cm per hour.
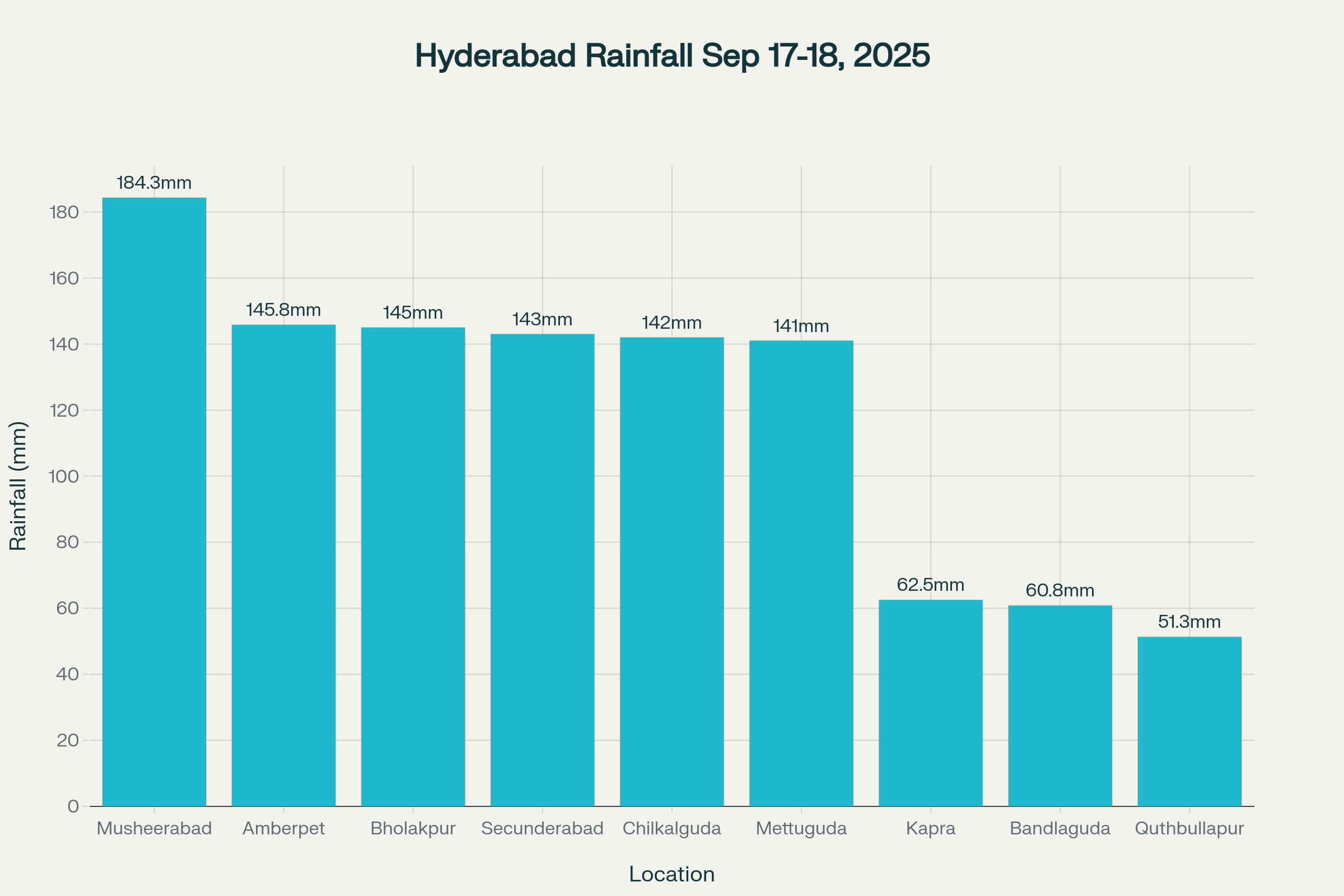
Rainfall distribution across Hyderabad areas during September 17-18, 2025 flooding event
- Extreme Rainfall Distribution: Bholakpur, Chilkalguda, Secunderabad, and Mettuguda all recorded over 140mm of precipitation in less than 24 hours
- Infrastructure Overwhelm: The sudden volume completely overwhelmed existing stormwater management systems across Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation limits
- Regional Impact: Areas like Kapra (62.5mm), Bandlaguda (60.8mm), and Quthbullapur (51.3mm) also reported significant flooding affecting low-lying residential colonies
The intensity of these Hyderabad floods has forced authorities to implement emergency traffic diversions, with underpasses including the Bible House location becoming completely inundated and impassable. Chief Minister A Revanth Reddy has directed all departments including Police, GHMC, HYDRAA, Traffic, and Energy to coordinate comprehensive relief operations while clearing waterlogged thoroughfares. The India Meteorological Department has issued continued warnings predicting heavy thunderstorms for Thursday night and Friday, raising concerns about additional Hyderabad floods in vulnerable low-lying areas.
Search Operations Continue for Missing Flood Victims
The human toll of ongoing Hyderabad floods continues to mount as search and rescue operations remain active for three individuals who went missing during separate incidents over the past week. Two men, identified as Arjun and Ramu, were swept away by the overflowing Afzalsagar nala in Mallepally area, while a third person fell into a nala in Musheerabad and has not been located despite intensive search efforts. The Hyderabad Disaster Response and Asset Protection Agency (HYDRAA) has deployed specialized teams with boats and diving equipment to conduct systematic searches of drainage channels and manholes throughout affected areas.
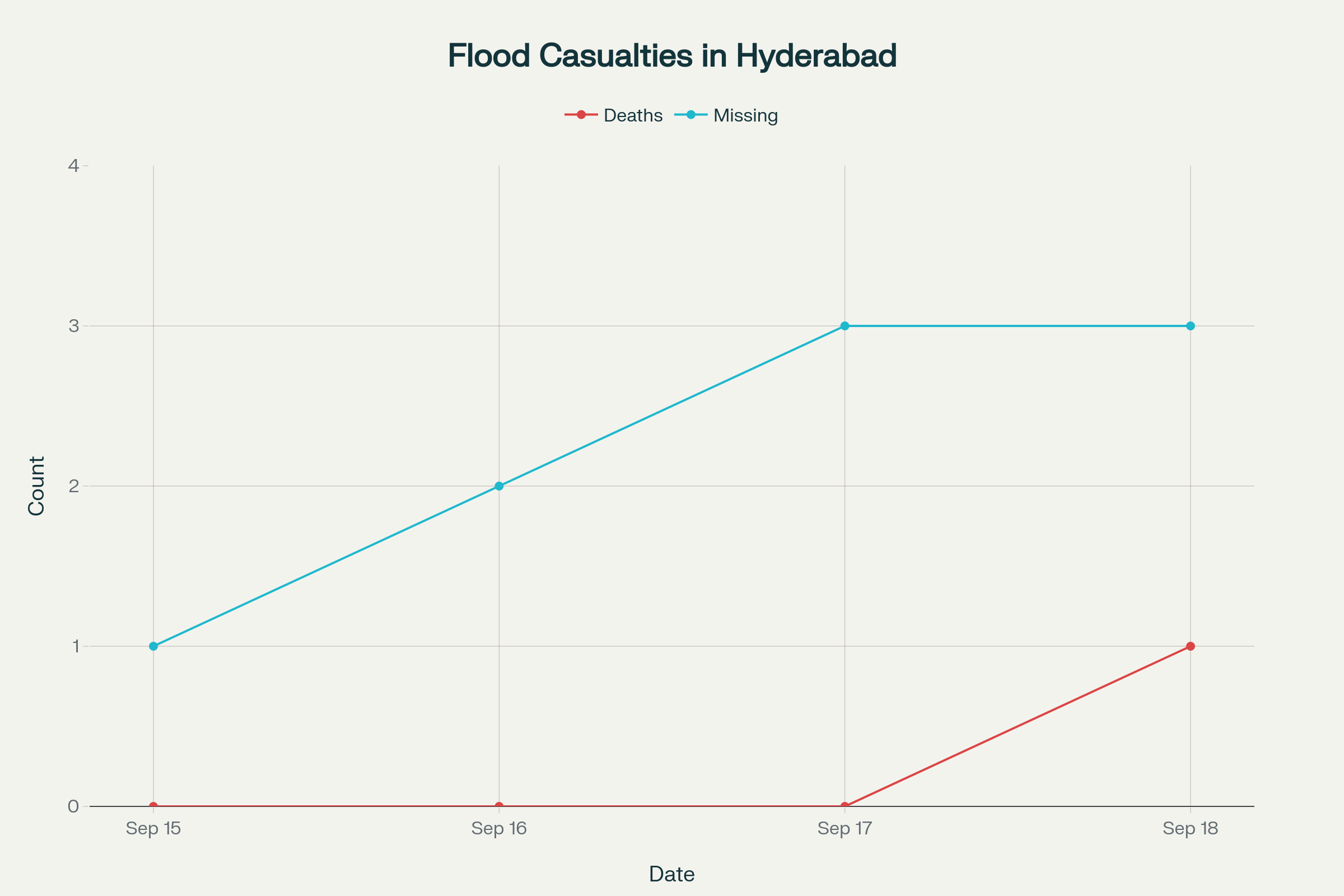
Timeline of flood casualties and missing persons in Hyderabad (September 15-18, 2025)
- Coordinated Search Efforts: HYDRAA teams are systematically checking manholes along drain networks where victims were last seen
- Technology Integration: Search operations utilize both ground teams and monitoring equipment to track potential locations of missing persons
- Resource Deployment: Multiple agencies including fire services, police, and municipal disaster response units are coordinating rescue activities
The complexity of search operations during active Hyderabad floods presents significant challenges for rescue teams, who must navigate dangerous conditions while maintaining hope for survivor recovery. Local residents have reported that repeated complaints about inadequate drainage infrastructure in affected areas had previously gone unaddressed, contributing to the severity of current flooding impacts. These ongoing search efforts underscore the critical need for enhanced flood preparedness and response capabilities as monsoon conditions continue to threaten the region with additional Hyderabad floods through the remainder of September.
Infrastructure Failures Expose Urban Planning Deficiencies
The recurring pattern of devastating Hyderabad floods reveals systemic infrastructure deficiencies that have plagued the city’s urban development for decades. Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation data indicates that the current drainage system, comprising both natural and artificial channels, was designed with a maximum capacity of approximately 650 square kilometers but has been severely compromised by rapid urbanization. Over the past 40 years, unchecked development has isolated more than two-thirds of the city’s 185 interconnected lakes, preventing natural stormwater redistribution that historically mitigated flood risks.
- Lake System Disruption: Originally interconnected water bodies that naturally managed monsoon runoff have been isolated by urban development
- Drainage Capacity Gap: Current infrastructure can handle only 2cm per hour rainfall, far below the 18cm recorded during recent storms
- Development Pressure: Rapid urbanization has reduced natural absorption areas while increasing impermeable surface coverage
The GHMC has recently approved a comprehensive stormwater master plan encompassing the Telangana Core Urban Region to address these structural deficiencies in flood management. This initiative includes implementing Geographic Information System-based flood mitigation measures, advanced 2D and 3D sensor networks, and sustainable solutions such as bioswales and rain gardens. However, the immediate crisis of ongoing Hyderabad floods demonstrates that these long-term infrastructure improvements cannot address current vulnerabilities faced by millions of residents during active monsoon periods.
Government Response and Emergency Management Coordination
State and municipal authorities have mobilized comprehensive emergency response protocols as Hyderabad floods continue to threaten public safety across the metropolitan region. The Telangana State Disaster Management Authority, recently reorganized under Chief Minister A Revanth Reddy’s leadership, has coordinated multi-departmental response efforts involving irrigation, electricity, health, agriculture, police, and transport agencies. Special nodal officers have been appointed for departments directly related to flood and rain management, creating a streamlined command structure for emergency coordination during active crisis periods.
- Multi-Agency Coordination: Integrated response involving GHMC, HYDRAA, Traffic Police, Fire Services, and Revenue Departments
- Real-Time Monitoring: Enhanced information systems provide scientific analysis of rainfall data and flood progression patterns
- Resource Mobilization: Emergency equipment including mobile pumps, rescue boats, and temporary shelters deployed across affected areas
The state government’s commitment to strengthening disaster management capabilities reflects lessons learned from previous catastrophic flooding events, including the devastating 2020 floods that claimed 33 lives and caused infrastructure damage worth Rs 6,000 crore. Current protocols emphasize proactive evacuation of residents from low-lying areas and continuous monitoring of water release from upstream reservoirs to minimize downstream flooding impacts. Despite these enhanced preparedness measures, the intensity and frequency of current Hyderabad floods continue to test the limits of emergency response capabilities while highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive urban flood resilience infrastructure.
Closing Assessment
The tragic death of Mohammed Sharfuddin represents not merely another casualty of severe weather, but a stark reminder of the systemic vulnerabilities that continue to plague Hyderabad’s flood management infrastructure during monsoon seasons. As search operations persist for three missing individuals and meteorological forecasts predict continued heavy rainfall through the weekend, the immediate priority remains coordinating emergency response efforts while addressing the underlying urban planning deficiencies that have made such devastating Hyderabad floods an annual reality.
The state’s enhanced disaster management protocols and GHMC’s comprehensive stormwater master plan offer hope for long-term resilience, but current events demonstrate that substantial infrastructure investment and implementation remain critical for protecting the 11 million residents of Greater Hyderabad from future flooding catastrophes.


