Key Highlights:
- Prime Minister Modi endorsed the ₹72,000-crore Great Nicobar Island Project as strategically vital for India’s maritime dominance in the Indian Ocean Region
- Union Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav defended the project against Congress criticism, emphasizing its role in balancing economy and ecology
- The comprehensive development plan spans 16,610 hectares and includes a 14.2 million TEU container terminal, international airport, and township for 65,000 residents
Opening Overview
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has thrown his full support behind the Great Nicobar Island Project, characterizing it as a transformative initiative of strategic, defense, and national importance that will establish India’s dominance in the Indian Ocean Region. The Prime Minister’s endorsement came as he shared an article by Union Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav defending the ambitious ₹72,000-crore infrastructure project against mounting criticism from Congress leaders. This ambitious development represents one of India’s most comprehensive maritime infrastructure undertakings, designed to leverage the island’s strategic position near the Malacca Strait, through which approximately 25% of global trade flows.
The Great Nicobar Island Project is of strategic, defence, and national importance, designed to transform the island into a major hub for maritime and air connectivity in the Indian Ocean Region.
— Bhupender Yadav (@byadavbjp) September 12, 2025
The decision to develop Great Nicobar Island has been taken after due… pic.twitter.com/EiO3ZbxcS1
The initiative has emerged as a defining element of India’s Maritime Vision 2030 and Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, positioning the southernmost island of the Andaman and Nicobar archipelago as a critical hub for trade, tourism, and military presence. With its equidistant location from major ports like Colombo, Port Klang, and Singapore, the Great Nicobar Island Project aims to capture 20-30% of regional cargo traffic currently dominated by foreign hubs. The project’s strategic importance has intensified amid China’s growing assertiveness in the Indo-Pacific region, making this development essential for India’s geopolitical objectives.
Strategic Maritime Infrastructure Development
The Great Nicobar Island Project centers on establishing India’s largest container transshipment terminal at Galathea Bay, with an impressive capacity of 14.2 million TEU (Twenty-Foot Equivalent Units) annually. This massive infrastructure component will rival Singapore’s transshipment capabilities, positioning India to challenge China’s influence over the Malacca Strait shipping lanes. The terminal represents the cornerstone of the maritime ambitions, designed to handle wide-body vessels and accommodate the world’s largest container ships.
- The International Container Transshipment Terminal will be developed in phases, starting with a 4 million TEU capacity in Phase I
- The facility will span across the eastern side of Galathea Bay, leveraging natural deep-water conditions for efficient port operations
Beyond the port infrastructure, the development includes a greenfield international airport with a 3,300-meter runway capable of handling wide-body aircraft. This dual-purpose facility will serve both civilian and defense requirements, with a projected peak capacity of 4,000 passengers per hour by 2050. The airport component strengthens India’s air connectivity across the Indian Ocean Region, providing strategic military positioning alongside commercial aviation benefits. The integrated approach ensures seamless connectivity between maritime and aviation infrastructure, creating a comprehensive logistics hub.
Economic and Urban Development Framework
The Great Nicobar Island Project encompasses extensive township development spanning 16,610 hectares, designed to accommodate up to 65,000 residents including workers, migrants, and support staff. This ambitious urban component will feature residential complexes, commercial zones, entertainment facilities, and institutional infrastructure to support the growing population. The township development represents a crucial element of the holistic approach, ensuring sustainable human settlement alongside industrial growth.
- The planned cities will be developed on both the southeast and southwest sides of Great Nicobar Island
- The township will include modern amenities such as shopping complexes, restaurants, healthcare facilities, and educational institutions
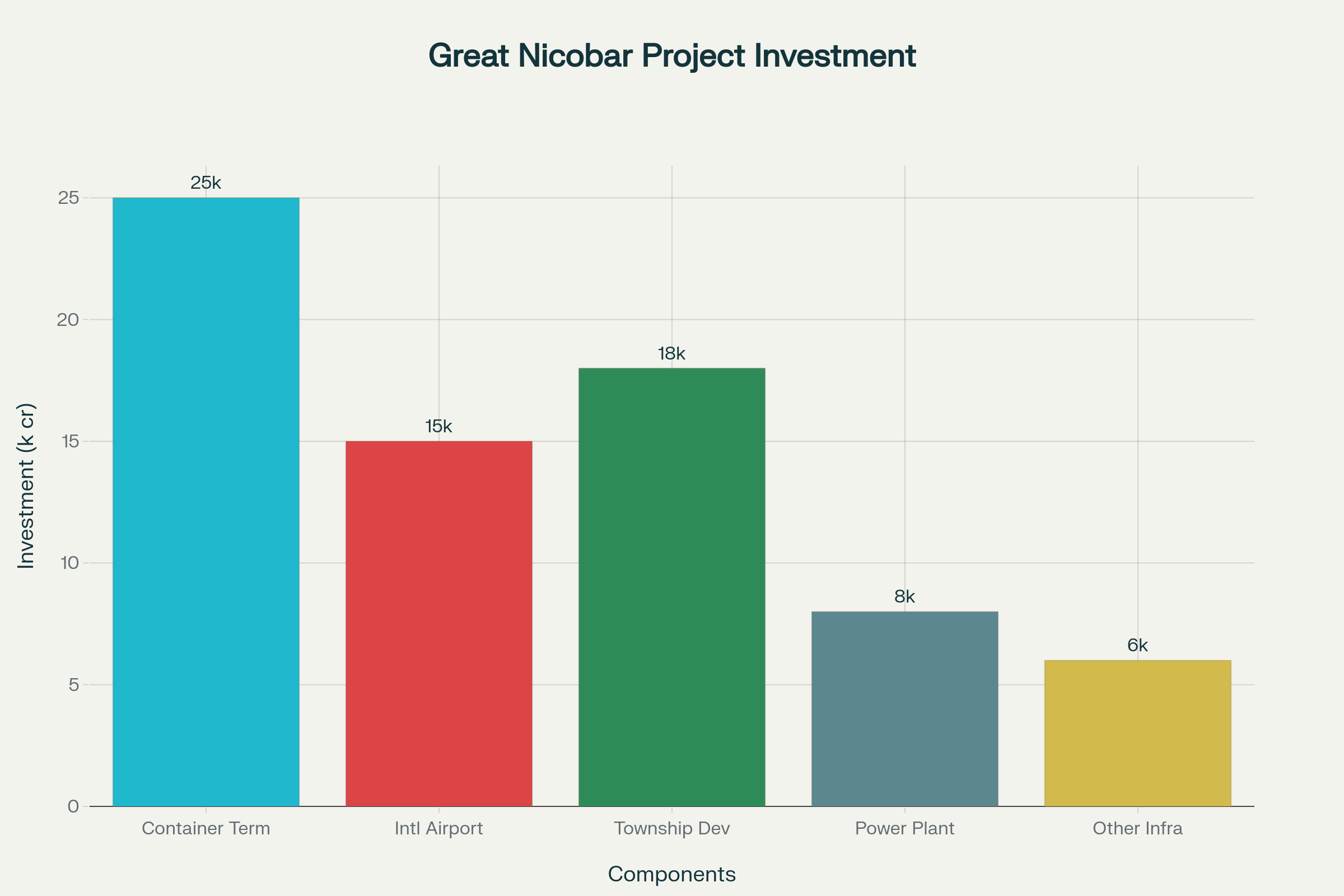
Investment Breakdown of the ₹72,000 Crore Great Nicobar Island Project by Major Components
The development incorporates a 450 MVA gas and solar-based power plant to ensure energy self-sufficiency for the entire infrastructure. This hybrid energy facility demonstrates the commitment to sustainable development while meeting the substantial power requirements of the port, airport, and township operations. The energy infrastructure will position the island as a model for renewable energy integration in large-scale infrastructure developments. Additional components include luxury tourism resorts, cruise ship terminals, and industrial hubs to diversify the economic base.
Government Implementation and Institutional Framework
The Great Nicobar Island Project is being implemented by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO), a government entity established in 1988 for the sustainable development of the territory. NITI Aayog conceptualized the initiative following a comprehensive feasibility study conducted by AECOM India, which identified the island’s strategic advantages for maritime commerce. The development received environmental and forest clearances in 2022, despite concerns raised by environmental groups about ecological impact.
- ANIIDCO has generated average annual revenues of ₹370 crore over the past three years, raising questions about its capacity to manage the massive infrastructure undertaking
- The corporation currently operates petroleum distribution, tourism resorts, and dairy businesses across the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Union Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav has emerged as the primary defender of the Great Nicobar Island Project, publishing detailed explanations of its strategic importance and environmental safeguards. His advocacy directly counters Congress leader Sonia Gandhi’s criticism that the development threatens tribal communities and unique ecosystems. The initiative has become a focal point of political debate, with the government emphasizing its role in India’s strategic positioning while opposition parties highlight environmental and social concerns. Minister Yadav maintains that the development poses no threat to tribal groups and incorporates comprehensive ecological protections.
Political Debate and Environmental Considerations
The Great Nicobar Island Project has sparked intense political controversy, with Congress Parliamentary Party Chairperson Sonia Gandhi denouncing it as a “planned misadventure” that threatens indigenous communities and fragile ecosystems. Gandhi’s criticism focuses on the estimated cutting of 8.5 lakh trees across 15% of the island’s landmass, representing one of India’s largest forest diversions. The opposition’s stance emphasizes potential ecological catastrophe and violations of tribal rights, challenging the government’s development narrative.
- The project area covers approximately 166 square kilometers, about 10% of Great Nicobar’s total 910 square kilometer area
- Environmental concerns include impacts on the Shompen and Nicobarese tribal communities, who number fewer than 1,000 people
In response to criticism, government officials assert that the Great Nicobar Island Project incorporates comprehensive environmental protection measures and tribal welfare provisions. The defense emphasizes its strategic necessity for India’s maritime security and economic growth, positioning environmental concerns as manageable challenges rather than insurmountable obstacles. Prime Minister Modi’s endorsement signals the government’s determination to proceed despite opposition criticism, framing it as essential for national interest. The debate reflects broader tensions between development imperatives and environmental conservation in contemporary India.
Closing Assessment
The Great Nicobar Island Project stands as a defining test of India’s ability to balance strategic ambitions with environmental stewardship and social responsibility. Prime Minister Modi’s emphatic support underscores its critical importance to India’s long-term geopolitical strategy in the Indo-Pacific region, where competition with China continues to intensify. The success could establish India as a dominant maritime power in the Indian Ocean, capturing significant portions of global shipping traffic while strengthening defense capabilities near crucial sea lanes.
Union Minister Shri @byadavbjp explains that the Great Nicobar Island Project, which is of strategic, defence and national importance, transforms the region into a major hub of maritime and air connectivity in the Indian Ocean Region. He highlights it as a prime example of… https://t.co/dgoPUHy2qa
— PMO India (@PMOIndia) September 12, 2025
However, the ultimate legacy will depend on the government’s ability to address legitimate environmental and social concerns while delivering promised economic benefits. The project’s scale and ambition reflect India’s growing confidence in pursuing transformative infrastructure initiatives, yet its implementation will require unprecedented coordination between economic development and ecological preservation. As the Great Nicobar Island Project moves forward, it will serve as a benchmark for India’s approach to balancing national security imperatives with sustainable development principles in the 21st century.


