Key Highlights:
- Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick confirms elimination of H-1B lottery system in favor of wage-based selection prioritizing higher-earning applicants
- Proposed “Gold Card” system offers permanent residency for $5 million investment, marking shift from traditional employment-based immigration
- Indian professionals face significant impact as they comprise over 70% of H-1B visa recipients annually
The Trump administration has announced a dramatic restructuring of America’s H-1B visa program, with Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick declaring the current system a “scam” that prioritizes foreign workers over Americans. This sweeping overhaul signals the most significant changes to skilled worker immigration policy in decades, potentially affecting millions of foreign professionals and students currently pursuing American careers.
The announcement comes as the administration prepares to replace the decades-old lottery-based H-1B visa system with a merit-driven approach that prioritizes higher-wage earners. Lutnick’s sharp criticism of the existing framework highlights the Trump administration’s commitment to fundamentally reshape how America attracts and retains international talent.
In a Fox News interview, Lutnick revealed his direct involvement in transforming both the H-1B visa and green card programs, stating: “I am involved in changing the H-1B programme because that is terrible. We are going to change the green card.” His comments reflect a broader policy shift toward what he terms “picking the best people to come into the country.”
The current H1B visa system is a scam that lets foreign workers fill American job opportunities.
— Howard Lutnick (@howardlutnick) August 26, 2025
Hiring American workers should be the priority of all great American businesses. Now is the time to hire American. pic.twitter.com/l27HEhF7C3
Wage-Based Selection System Set to Replace Lottery Model
The most significant change involves eliminating the current lottery system that has governed H-1B visa allocations since its inception. Under the proposed wage-based model, applications from higher-earning professionals will receive priority, fundamentally altering the competitive landscape for skilled foreign workers.
- Current lottery system treats all qualified applications equally regardless of salary level
- New wage-based approach prioritizes candidates earning above-average wages for their positions
This transformation addresses longstanding criticism that the H-1B visa program allows companies to hire foreign workers at below-market rates. Lutnick specifically cited wage disparities, noting that the average American earns $75,000 annually while the average green card recipient makes $66,000, describing this as “taking the bottom quartile.”(2)(4)(5)
The policy shift represents a direct response to concerns that the current H-1B visa system undermines American workers’ earning potential while enabling companies to access cheaper foreign labor. Administrative officials argue that prioritizing higher-wage applications will ensure that foreign workers complement rather than compete with domestic talent.
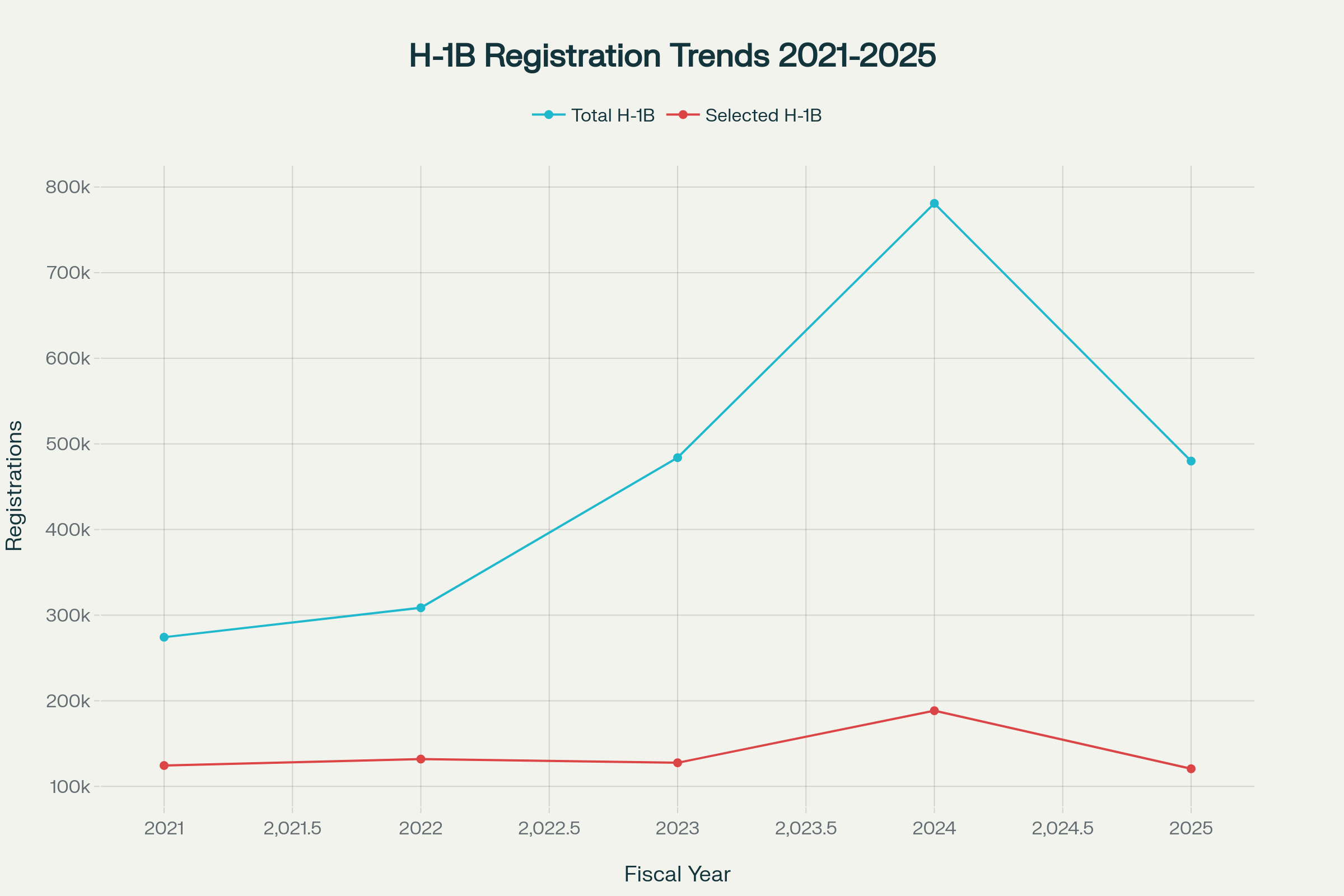
Recent H-1B visa registration data reveals the program’s massive scale and growing demand. The fiscal year 2024 saw a record 780,884 total registrations, with 188,400 applications selected. However, fiscal year 2025 showed a decline to 479,953 registrations with 120,603 selections, indicating market adjustments in response to anticipated policy changes.
“Gold Card” Initiative Targets Wealthy Investors
Alongside H-1B visa reforms, the administration is developing a “Gold Card” program offering permanent residency to foreign investors contributing $5 million to the US economy. This initiative represents a departure from traditional employment-based immigration pathways, emphasizing capital investment over skilled labor.
- Gold Card program requires $5 million investment for permanent residency
- System aims to attract wealthy individuals rather than traditional skilled workers
The Gold Card concept reflects broader immigration policy priorities focused on economic contribution rather than employment relationships. Unlike the H-1B visa program, which requires employer sponsorship and temporary status, the Gold Card would provide immediate permanent residency for qualifying investors.
This dual approach—restricting traditional work visas while expanding investor pathways—signals the administration’s preference for immigration policies that directly inject capital into the American economy. The Gold Card initiative essentially creates a premium tier of immigration reserved for ultra-wealthy applicants.
Administrative officials view the Gold Card as complementing rather than replacing the reformed H-1B visa system. While skilled workers must navigate increasingly competitive wage-based selection, wealthy investors can bypass traditional immigration queues entirely through substantial financial commitments.
Impact on Indian Professionals and Technology Sector
Indian nationals face the most significant consequences from H-1B visa program changes, given their dominant representation in current allocations. Data consistently shows Indians receiving over 70% of annual H-1B visas, making them disproportionately affected by any policy modifications.
- Indian professionals comprise over 70% of H-1B visa recipients annually
- Technology sector heavily relies on Indian talent for specialized roles
The wage-based selection system particularly impacts early-career Indian professionals and graduates from smaller firms offering lower initial salaries. While senior-level Indian executives earning premium wages may continue securing visas, mid-level workers and recent graduates will face substantially reduced opportunities.
Technology companies employing large numbers of H-1B visa holders are already considering offshore alternatives in response to proposed changes. Industry analysis suggests that firms may expand operations in India or increase remote work arrangements to maintain access to Indian technical talent without navigating restrictive visa requirements.
The transformation affects not only current H-1B visa holders but also Indian students pursuing American education with hopes of eventual work authorization. Traditional pathways from student visas to H-1B status become increasingly uncertain under merit-based selection criteria that favor established high earners over entry-level professionals.
| Fiscal Year | Total H-1B Registrations | Selected H-1B Registrations |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 274,237 | 124,415 |
| 2022 | 308,613 | 131,924 |
| 2023 | 483,927 | 127,600 |
| 2024 | 780,884 | 188,400 |
| 2025 | 479,953 | 120,603 |
Additional Policy Changes Tighten Immigration Enforcement
Beyond the fundamental H-1B visa restructuring, the administration has implemented additional measures affecting foreign workers. The closure of the Office of Citizenship and Immigration Services Ombudsman eliminated a crucial resource that previously assisted thousands of immigrants with visa-related issues.
- CIS Ombudsman office closure removes immigrant assistance services
- New biometric and address reporting requirements increase compliance burden
Current H-1B visa holders now face enhanced reporting requirements, including providing biometric information and maintaining updated home addresses with immigration authorities. These measures represent a significant departure from previous practices that focused primarily on employment authorization rather than detailed personal monitoring.
Vice President JD Vance’s statement that green cards do not provide “indefinite right to stay in the United States” has further complicated the immigration landscape for foreign professionals. This position suggests potential future restrictions on permanent residency renewals or conversions, adding uncertainty to long-term career planning for H-1B visa holders.
The cumulative effect of these policy changes creates a more restrictive environment for foreign workers at all levels. From initial visa applications through permanent residency processes, immigrants face increased scrutiny, higher barriers, and reduced certainty about their ability to remain in the United States long-term.
Recent research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst reveals that immigrants in the United States earn 10.6% less than similarly educated native-born workers, with job access barriers rather than wage discrimination accounting for the majority of this gap. This data provides context for the administration’s emphasis on wage-based H-1B visa selection as a mechanism to ensure foreign workers earn competitive salaries.
Closing Assessment
The Trump administration’s overhaul of the H-1B visa system represents the most significant shift in skilled immigration policy in recent decades. By replacing lottery-based selection with wage-driven criteria, the administration aims to ensure that foreign workers complement rather than compete with domestic talent at comparable salary levels.
The simultaneous introduction of the Gold Card program for wealthy investors creates a two-tiered immigration system that distinguishes between traditional skilled workers and high-net-worth individuals. This approach reflects broader policy priorities that emphasize immediate economic contribution over long-term employment relationships.
For the millions of foreign professionals currently navigating the H-1B visa process, these changes introduce substantial uncertainty and increased competition. While high-earning applicants may benefit from the merit-based approach, early-career professionals and those at smaller companies face diminished prospects for American work authorization.
The ultimate impact of these H-1B visa reforms will depend on implementation details and industry adaptation strategies. As companies and workers adjust to the new reality, the effectiveness of wage-based selection in achieving stated policy goals will become apparent through future application and approval patterns.


