Key Highlights:
- Global health agencies introduce new diagnostic criteria lowering PPH detection threshold from 500ml to 300ml blood loss when combined with abnormal vital signs
- E-MOTIVE treatment bundle implementation shows 96.9% effectiveness rate in clinical trials across 23 countries
- New guidelines could prevent tens of thousands of maternal deaths annually, with Sub-Saharan Africa accounting for 70% of global fatalities
Opening Overview
World Health Organization, International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics, and International Confederation of Midwives have released groundbreaking guidelines that could revolutionize postpartum hemorrhage prevention and treatment globally. The comprehensive recommendations, published October 5, 2025, introduce critical changes to diagnostic criteria and treatment protocols for postpartum hemorrhage, the leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide.
Postpartum haemorrhage is one of the leading causes of maternal mortality globally.
— World Health Organization (WHO) (@WHO) October 6, 2025
Even when not fatal, it can lead to lifelong physical and mental health impacts, from major organ damage to hysterectomies, anxiety and trauma.
It is highly treatable if caught early… pic.twitter.com/5mw0I6u5FX
These evidence-based guidelines stem from the largest study on postpartum hemorrhage to date, analyzing data from over 300,000 women across 23 countries. The new approach emphasizes early detection at 300ml blood loss combined with abnormal vital signs, rather than waiting for the traditional 500ml threshold. With postpartum hemorrhage causing approximately 45,000 maternal deaths annually out of 260,000 total maternal fatalities, these guidelines represent a pivotal advancement in maternal healthcare.
Postpartum haemorrhage – excessive bleeding after childbirth – affects millions of women annually and causes nearly 45,000 deaths.
— World Health Organization (WHO) (@WHO) October 6, 2025
Better prevention, early diagnosis and rapid treatment are critical for saving lives.
New WHO guidelines https://t.co/4PvzXn5hAP pic.twitter.com/FD0f3A2vdP
The timing proves particularly crucial as global maternal mortality reduction has stagnated since 2016, with progress declining to just 1.5% annually instead of the 15% reduction needed to meet UN Sustainable Development Goals. Healthcare systems worldwide now have access to 51 evidence-based recommendations designed to maximize impact where resources are most limited.
Enhanced Diagnostic Framework
The revolutionary diagnostic approach represents the most significant advancement in postpartum hemorrhage detection methodology in decades. Traditional diagnostic criteria required blood loss of 500ml or more, often resulting in delayed intervention when women were already experiencing severe complications. The new guidelines advocate for immediate action when blood loss reaches 300ml and abnormal vital signs are observed, enabling healthcare providers to intervene before postpartum hemorrhage becomes life-threatening.
- Clinical studies demonstrate that measured blood loss below conventional thresholds, combined with hemodynamic signs, accurately predicts women at risk of death or severe complications
- Implementation requires calibrated drapes for precise blood loss measurement, ensuring objective assessment rather than visual estimation
- Healthcare providers must monitor women closely after birth, checking vital signs regularly to identify early warning indicators
Research published simultaneously in The Lancet validates this approach through individual participant data meta-analysis involving over 300,000 deliveries. The study confirms that earlier detection significantly improves outcomes for women experiencing postpartum hemorrhage, particularly in resource-limited settings where delays in treatment often prove fatal. This evidence-based framework addresses the reality that many postpartum hemorrhage cases occur without identifiable risk factors, making early detection and rapid response absolutely critical.

Healthcare systems implementing these diagnostic criteria can expect improved identification of at-risk patients, reduced severe morbidity rates, and decreased postpartum hemorrhage-related mortality. The guidelines specifically address challenges in overstretched healthcare facilities where staff may lack time for continuous monitoring, providing practical tools for systematic assessment.
E-MOTIVE Treatment Protocol
The E-MOTIVE bundle represents a standardized, evidence-based approach to postpartum hemorrhage treatment that has demonstrated remarkable effectiveness across diverse healthcare settings. This systematic intervention protocol consists of six sequential components designed for immediate deployment upon postpartum hemorrhage diagnosis. Clinical trials show 96.9% implementation success rates, with significantly improved outcomes compared to usual care approaches.
- Massage of the uterus provides immediate mechanical stimulation to promote uterine contraction and reduce bleeding
- Oxytocic drugs, preferably oxytocin or heat-stable carbetocin, stimulate sustained uterine contractions
- Tranexamic acid administration reduces bleeding through antifibrinolytic mechanisms, proven effective in multiple studies
The protocol continues with intravenous fluid resuscitation to maintain hemodynamic stability, thorough vaginal and genital tract examination to identify trauma sources, and systematic escalation of care if bleeding persists. Research demonstrates that E-MOTIVE intervention reduces composite severe morbidity risk ratios significantly compared to standard care protocols. The bundle approach ensures no critical steps are overlooked during high-stress emergency situations, providing healthcare workers with clear, actionable guidance.

Implementation studies across multiple countries reveal that the E-MOTIVE protocol improves postpartum hemorrhage-related outcomes among women delivering vaginally, with particular benefits in low-resource settings. The systematic approach addresses the reality that postpartum hemorrhage can escalate with alarming speed, requiring immediate, coordinated intervention to prevent maternal death.
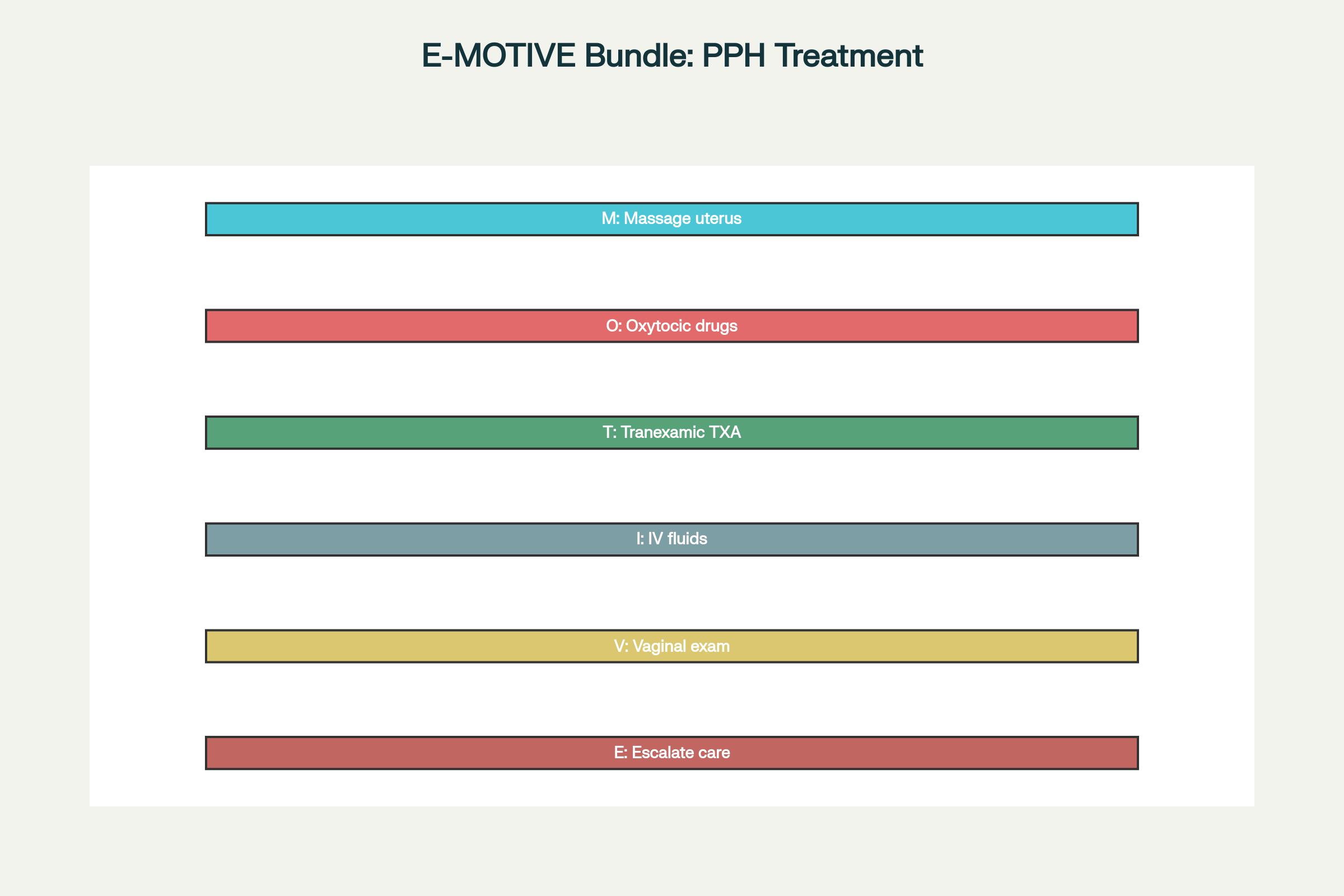
E-MOTIVE Bundle: Six-Step Protocol for Postpartum Hemorrhage Treatment
Prevention and Risk Mitigation
Effective postpartum hemorrhage prevention requires comprehensive antenatal and postnatal care addressing modifiable risk factors that increase bleeding likelihood. The guidelines emphasize addressing anemia, which affects approximately 57% of pregnant women in many low and middle-income countries and significantly worsens postpartum hemorrhage outcomes. Research from Sub-Saharan Africa demonstrates that anemia prevention strategies can substantially reduce postpartum hemorrhage mortality rates.
- Daily oral iron and folate supplementation during pregnancy reduces anemia prevalence and associated bleeding risks
- Intravenous iron transfusions provide rapid correction when oral therapy fails or immediate treatment is needed
- Perineal massage during late pregnancy reduces trauma likelihood and subsequent bleeding complications
The prevention framework discourages unsafe practices such as routine episiotomies while promoting evidence-based techniques that reduce bleeding risk. During the third stage of labor, administration of quality-assured uterotonics, preferably oxytocin or heat-stable carbetocin alternatives, supports proper uterine contraction. When intravenous options are unavailable and cold chain reliability is compromised, misoprostol may serve as a last resort option.
Regional data from Sub-Saharan Africa reveals that postpartum hemorrhage affects up to 16.5% of deliveries, with anemia and thrombocytopenia serving as prominent risk factors. Prevention strategies must address these underlying health conditions through improved nutritional support, malaria prevention, and comprehensive antenatal care programs. The guidelines recognize that effective prevention requires investment in health systems infrastructure, education, and supply chains for essential medicines.
Global Implementation and Impact
The implementation framework addresses the stark disparity in postpartum hemorrhage outcomes between high-income and low-resource settings. Sub-Saharan Africa accounts for approximately 70% of global maternal deaths, with maternal mortality ratios ranging from 500 to 1,000 per 100,000 births compared to 5-20 in developed countries. These guidelines specifically target regions where postpartum hemorrhage burden is highest and healthcare resources most constrained.
- Training and implementation resources developed with UNFPA provide practical modules for frontline health workers
- National-level guides facilitate introduction of new practices within existing healthcare systems
- Simulation-based training strengthens emergency response capabilities in resource-limited settings
The guidelines launch coincides with establishment of World PPH Day on October 5, sending a clear message that no woman should die from preventable postpartum hemorrhage. Implementation success requires coordinated action from governments, health systems, donors, and partners to adopt recommendations quickly and invest in maternal care infrastructure. The Global Roadmap to Combat Postpartum Hemorrhage 2023-2030 provides strategic framework for sustained progress.
Current progress toward UN Sustainable Development Goal 3.1, which targets global maternal mortality below 70 per 100,000 live births by 2030, remains insufficient. The global maternal mortality ratio stands at 197 per 100,000 in 2023, requiring dramatic acceleration in improvement rates. These postpartum hemorrhage guidelines represent a crucial tool for achieving these ambitious targets, particularly in countries where maternal deaths remain unacceptably high.
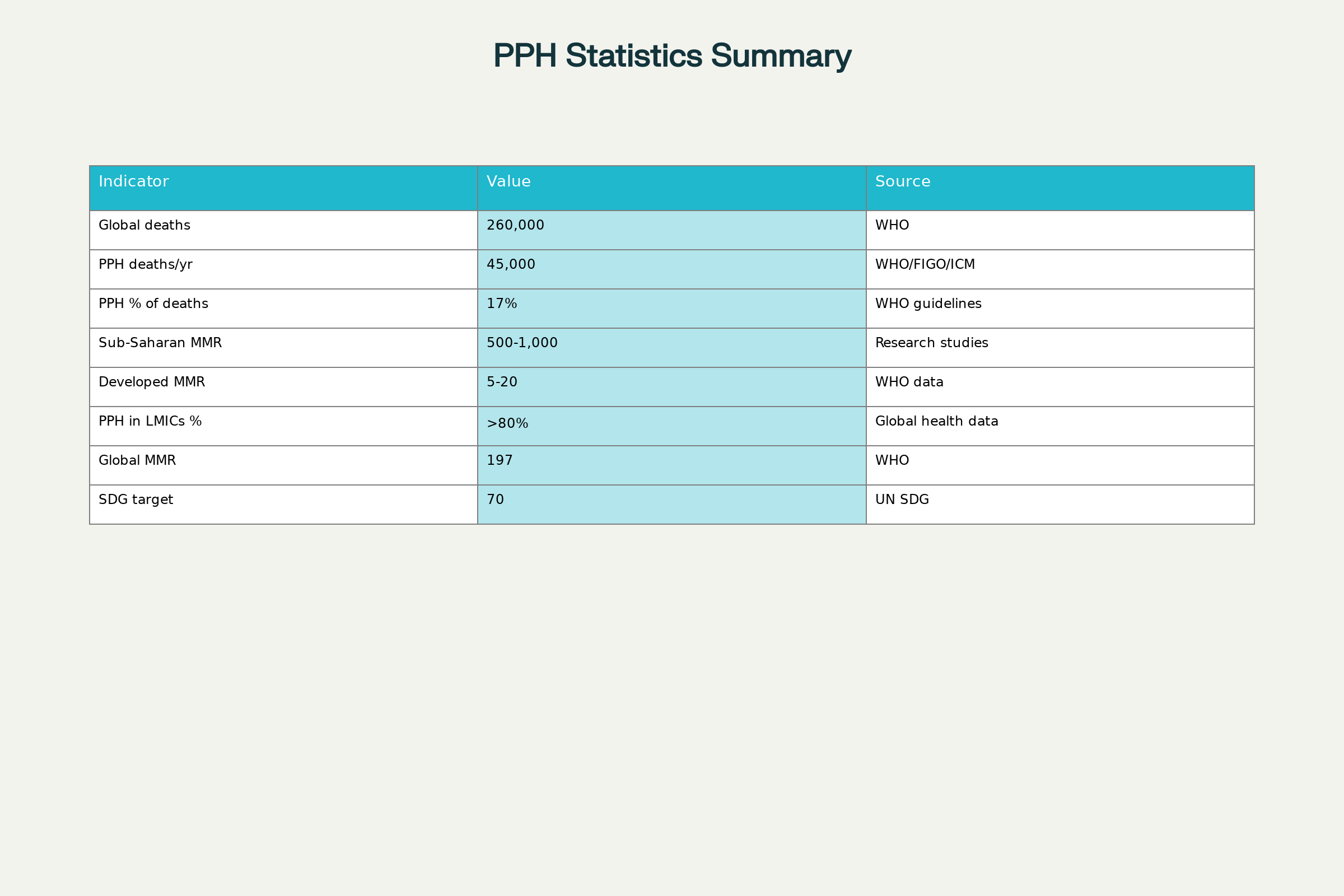
Global Postpartum Hemorrhage and Maternal Mortality Statistics (2023-2025)
Closing Assessment
The WHO, FIGO, and ICM guidelines mark a transformative moment in global maternal health, offering evidence-based solutions to address postpartum hemorrhage, the world’s leading cause of maternal mortality. With 45,000 women dying annually from postpartum hemorrhage, these comprehensive recommendations provide healthcare systems worldwide with practical tools to save lives and prevent lifelong complications. The integration of early diagnostic criteria, standardized treatment protocols, and prevention strategies creates a holistic approach to postpartum hemorrhage management that addresses the full spectrum of care.
Success depends on rapid implementation across healthcare systems, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia where the burden remains heaviest. The guidelines represent more than clinical recommendations; they embody a commitment to ending preventable maternal deaths and achieving health equity for women worldwide. As healthcare providers, policymakers, and international organizations embrace these evidence-based protocols, the vision of eliminating postpartum hemorrhage deaths moves from aspiration to achievable reality.


